NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Biology. Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom.
NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1. In some animal groups, the body is found divided into compartments with serial repetition of at least some organs. This characteristic feature is called
(a) Segmentation (b) Metamerism
(c) Metagenesis (d) Metamorphosis
Ans: (b) Metamerism: In some animals, the body is externally and internally divided into segments with a serial repetition of at least some organs. For example, in earthworm, the body shows this pattern called metameric segmentation and the phenomenon is known as metamerism or true segmentation. Metamerism is found in 3 animal phylums—Annelida, Arthropoda and Chordata.
Q2. Given below are the types of cells present in some animals. Which of the following cells can differentiate to perform different functions?
(a) Choanocytes (b) Interstitial cells
(c) Gastrodermal cells (d) Nematocytes
Ans: (b) Interstitial cells can differentiate to perform different functions. Choanocytes is the characteristics cells of porifera.
Gastrodermal cells and Nematocytes are found in Hydra.
Q3. Which one of the following sets of animals share a four chambered heart?
(a) Amphibian, Reptiles, Birds (b) Crocodiles, Birds, Mammals
(c) Crocodiles, Lizards, Turtles (d) Lizards, Mammals, Birds
Ans: (b) Crocodiles, Birds, Mammals are the set of animals that share a four chambered heart
• Amphibian—two chambered heart
• Reptiles and lizards—three chambered heart except crocodiles
Q4. Which of the following pairs of animals has non-glandular skin?
(a) Snake and Frog (b) Chameleon and Turtle
(c) Frog and Pigeon (d) Crocodile and Tiger
Ans: (b) Chameleon and Turtle has non-glandular skin.
Q5. Birds and mammals share one of the following characteristics as a common feature.
(a) Pigmented skin (b) Pneumatic bones
(c) Viviparity (d) Warm blooded nature
Ans: (d) Birds and mammals both are warm blooded.
Q6. Which one of the following sets of animals belong to a single taxonomic group?
(a) Cuttlefish, Jellyfish, Silverfish, Dogfish, Starfish
(b) Bat, Pigeon, Butterfly
(c) Monkey, Chimpanzee, Man
(d) Silkworm, Tapeworm, Earthworm
Ans: (c) Monkey, Chimpanzee and Man belong to a single taxonomic group mammalia (class).
Q7. Which one of the following statements is incorrect? ,
(a) Mesoglea is present in between ectoderm and endoderm in Obelia
(b) Asterias exhibits radial symmetry
(c) Fasciola is a pseudocoelomate animal
(d) Taenia is a triploblastic animal
Ans: (c) Fasciola is an acoelomate animal.
Q8. Which one of the following statements is incorrect?
(a) In cockroaches and prawns excretion of waste material occurs through Malpighian tubules.
(b) In ctenophore, locomotion is mediated by comb plates.
(c) In Fasciola flame cells take part in excretion.
(d) Earthworms are hermaphrodites and yet cross fertilization take place among them.
Ans: (a)
• In cockroaches excretion of waste material occurs through Malpighian tubules.
• In prawns excretion of waste material occurs through green glands or antennal glands.
Q9. Which one of the following is oviparous?
(a) Platypus (b) Flying fox (Bat)
(c) Elephant (d) Whale
Ans: (a) Prototherians have evolved from reptiles. Mammary gland lacks nipples or teats.Corpus callosum is absent. Prototherians are oviparous/egg laying mammals. E.g.: Omithorynchus (Duck-billed platypus) is monotreme mammal.
Q10. Which one of the following is not a poisonous snake?
(a) Cobra (b) Viper (c) Python (d) Krait
Ans: (c) Python (Ajgar) is a non-poisonous snake. Poisonous snakes: Naja (Cobra), Bangarus coeruleus (Krait), Vipera (Viper), Hydrophis (Sea snake)
Najahaunaha: King Cobra. King Cobra is only snake which builds its nest. Nest forming snake is terrestrial and poisonous.
Q11. Match the following list of animals with their level of organization.
| Division of Labour | Animal | ||
| A. | Organ level | (i) | Pheretima |
| B. | Cellular aggregate level | (ii) | Fasciola |
| C. | Tissue level | (iii) | Spongilla |
| D. | Organ system level | (iv) | Obelia |
Choose the correct match showing division of labour with animal example.
- B—(i), C—(ii), D—(iii), A—(iv)
- B—(i), D—(ii), C—(iii), A—(iv)
- D—(i), A—(ii), B—(iii), C—(iv)
- A—(i), D—(ii), C—(iii), B—(iv)
Ans. (c)
| A. | Organ level | (ii) | Fasciola |
| B. | Cellular aggregate level | (iii) | Spongilla |
| C. | Tissue level | (iv) | Obelia |
| D. | Organ system level | (i) | Pheretima |
Q12. Body cavity is the cavity present between body wall and gut wall. In some animals the body cavity is not lined by mesoderm. Such animals are called (a) Acoelomate (b) Pseudocoelomate .
(c) Coelomate (d) Haemocoelomate
Ans: (b)
(i) Acoelomate: The animals in which the body cavity is absent are
called acoelomates, e.g.: Porifers, Coelentrates, Ctenophores and Platyhelminthes. .
(ii) Pseudocoelomate: In some animals, the body cavity is not lined by mesoderm, instead,the mesoderm is present as scattered pouches in between the ectoderm and endoderm. Here body cavity is directly connected to archenteron. Such a body cavity is called pseudocoelom and the animals possessing them are called pseudocoelomates. E.g.: Aschelminthes (Ascaris). Pseudocoelom is derived from blastocoel.
(iii) Coelomate: The body cavity, which is lined by mesoderm (on both sides) is called coelom. Animals possessing coelom are called coelomates, or coelom is cavity between alimentary canal and body wall enclosed by mesoderm on both sides. E.g.: Annelids, Arthropods, Molluscs, Echinoderms, Hemichordates and Chordates.
Depending upon its origin, true coelom or eucoelom is of two types:
(a) Schizocoelous: The coelom is formed by splitting of mesoderm. E.g.: Annelida, Arthropoda and Mollusca.
Note: The cavity filled with blood is called haemocoel. It is found in Arthropods (cockroach) and Molluscs (Pila).
(b) Enterocoelom: The coelom develops as an outgrowth of the enteron or embryonic gut. E.g.: Deuterostomia (Echinodermata and Chordata). Echinodermata is an enterocoelomate invertebrate.
Q13. Match the column A with column B and choose the correct option.
| Column A | Column B | ||
| A. | Porifera | (i) | Canal system |
| B. | Aschelminthes | (ii) | Water-vascular system |
| C. | Annelida | (iii) | Muscular Pharynx |
| D. | Arthropoda | (iv) | Jointed appendages |
| E. | Echinodermata | (v) | Metamers |
- A—(ii), B—(iii), C—(v), D—(iv), E—(i)
- A—(ii), B—(v), C—(iii), D—(iv), E—(i)
- A—(i), B—(iii), C—(v), D—(iv), E—(ii)
- A—(i), B—(v), C—(iii), D—(iv), E—(ii)
Ans: (c)
| A. | Porifera | (i) | Canal system . |
| B. | Aschelminthes | (iii) | Muscular Pharynx |
| C. | Annelida | (v) | Metamers |
| D. | Arthropoda | (iv) | Jointed appendages |
| E. | Echinodermata | (ii) | Water-vascular system |
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1. Identify the phylum in which adults exhibit radial symmetry and larva exhibit bilateral symmetry.
Ans: In phylum echinodermata, adults show radial symmetry whereas larva show bilateral symmetry.
Q2. What is the importance of pneumatic’ bOnes and air sacs in Aves?
Ans: Pneumatic bones in Aves keep the body light and thus help in flight. Air sacs help in respiration and buoyancy.
Q3. What is metagenesis? Mention an example which exhibits this phenomenon.
Ans: Alteration of generation is known as metagenesis. Obelia exhibits this phenomenon.
Q4. What is the role of feathers?
Ans: Feathers keep the body light and thus help in flight.
Q5. Which group of chordates possess sucking and circular mouth without jaws?
Ans: Cyclostomes have a sucking and circular mouth without jaws.
Q6. Give one example each for an animal possessing placoid scales and that with cycloid scales.
Ans: Placoid scales—Pristis, Trygon, Torpedo. Cycloid scales—Labeo Catla, Clarias
Q7.Mention two modifications in reptiles required for terrestrial mode of life.
Ans: 1. Their body is covered by dry and comified skin, epidermal scales or scutes.
2. Cleidoic eggs
Q8. Mention one example each for animals with chitinous exoskeleton and those covered by a calcareous shell.
Ans: The body of arthropods (like cockroach) is covered by chitinous exoskeleton and molluscan (like Pila) body is covered by a calcareous shell.
Q9. What is the role of radula in molluscs?
Ans: Radula is a file-like rasping organ help in feeding.
Q10. Name the animal, which exhibits the phenomenon of bioluminescence. Mention the phylum to which it belongs.
Ans: Bioluminescence (the property of a living organism to emit light) is well- marked in ctenophores.
Examples: Pleurobrachia, Ctenoplana, Beroe, Coeloplana and Velamen.
Q11. Write one example each of the following in the space provided.
a. Cold blooded animal
b. Warm blooded animal
c. Animal possessing dry and comified skin
d. Dioecious animal
Ans: Examples:
a. Cold blooded animal: amphibians (Frog)
b. Warm blooded animal: mammals (Human)
c. Animal possessing dry and comified skin: reptiles (Lizard)
d. Dioecious animal: aschelminthes (Ascaris)
Q12. Differentiate between a diploblastic and a triploblastic animal.
Ans: (i) Diploblastic: Animals in which the cells are arranged in two embryonic layers, an external ectoderm and an internal endoderm, are called diploblastic animals, e.g. Porifers, coelenterates and ctenophores.
(ii) Triploblastic: Those animals in which the developing embryo has a third germinal layer, mesoderm, in between the ectoderm and endoderm, are called triploblastic animals. E.g.: Platyhelminthes to Chordates.
Q13. Give an example for the following:
a. Roundworm
b. Fish possessing poison sting
c. A limbless reptile/amphibian .
d. An oviparous mammal
Ans: Examples:
a. Roundworm: Ascaris
b. Fish possessing poison sting: Trygon
c. A limbless reptile/ amphibian: Snakelfcthyophis
d. An oviparous mammal: Ornithorynchus (Duck-billed platypus)
Q14. Provide appropriate technical term in the space provided.
a. Blood-filled cavity in arthropods _________
b. Free-floating form of cnidaria _________
c. Stinging organ of jelly fishes _________
d. Lateral appendages in aquatic annelids _________
Ans: Provide appropriate technical term in the space provided.
a. Blood-filled cavity in arthropods: Haemocoel
b. Free-floating form of cnidaria: Medusa
c. Stinging organ of jelly fishes: Nematocyst
d. Lateral appendages in aquatic annelids: Parapodia
Q15. Match the following:
| Animals | Locomotory organ | ||
| a. | Octopus – | (i) | Limbs |
| b. | Crocodile | (ii) | Comb plates |
| c. | Catla | (iii) | Tentacles |
| d. | Ctenoplana | (iv) | Fins |
Ans:
| Animals | Locomotory organ | ||
| a.’ | Octopus | (iii) | Tentacles |
| b. | Crocodile | (i) | Limbs |
| c. | Catla | (iv) | Fins |
| d. | Ctenoplana | (ii) | Comb plates |
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1. Differentiate between:
a. Open circulatory system and closed circulatory system
b. Oviparous and viviparous characteristic
c. Direct development and Indirect development
Ans: a. Open Circulatory System and Closed Circulatory System:
| Open Circulatory System | Closed Circulatory System |
| The blood is pumped out of the heart into sinuses and the cells and tissues are directly bathed in it. | The blood is circulated within a network of vessels. |
b. Oviparous and Viviparous:
| Oviparous | Viviparous |
| Animals which lay eggs are called oviparous. | Animals which give birth to their young ones are called viviparous. |
C. Direct Development and Indirect Development:
| Direct Development | Indirect Development |
| Animals which do not have a larval stage in their development are said to exhibit direct development. | Animals which have a larval stage, which do not resemble the adult in their development are said to exhibit indirect development |
Q2. Sort out the animals on the basis of their symmetry (radial or bilateral) coelenterates, ctenophores, annelids, arthropods, and echinoderms.
Ans: Coelenterates: Radial Ctenophores: Radial Annelids: Bilateral Arthropods: Bilateral Echinoderms: Radial
Q3. There has been an increase in the number of chambers in heart during evolution of vertebrates. Give the names of the class of vertebrates having two, three or four-chambered heart.
Ans: Two chambered heart: chondrichthyes and osteichthyes
Three chambered heart: Amphibia and Reptilia
Four chambered heart: Aves and mammalia
Q4. Fill up the blank spaces appropriately.
| Phylum/
Class |
Excretory
Organ |
Circulatory
Organ |
Respiratory
Organ |
| Arthropoda | A | B . | Lungs/Gills/ Tracheal System |
| C | Nephridia | Closed | Skin/Parapodia |
| D | Metanephridia | Open | E |
| Amphibia | F | Closed | Lung |
Ans.
A = Malpighian Tubule/ coxal glands/
antemary glands/ green glands
B = Open
C = Annelida
D = Mollusca
E = Feather like gills
F = Kidney
Q5. Match the following:
| a. | Amphibia | (i) | Air bladder |
| b. | Mammals | (ii) | Cartilagenous notochord |
| c. | Chondrichthyes | (hi) | Mammary glands |
| d. | Osteichthyes | (iv) | Pneumatic bones |
| e. | Cyclostomata | (v) | Dual habitat |
| f. | Aves | (vi) | Sucking and circular mouth without jaws |
Ans:
| a. | Amphibia | (v) | Dual habitat |
| b. | Mammals | (iii) | Mammary glands |
| c. | Chondrichthyes | (ii) | Cartilagenous notochord |
| d. | Osteichthyes | (i) | Air bladder |
| e. | Cyclostomata | (vi) | Sucking and circular mouth without jaws |
| f. | Aves | (iv) | Pneumatic bones |
Q6. Endoparasites are found inside the host body. Mention the special structure, possessed by these and which enables them to survive in those conditions.
Ans: The life cycles of endoparasities are more complex because of their extreme specialisation. Their morphological and anatomical features are greatly simplified while emphasizing their reproductive potential.
In accordance with their life style parasites evolve special adaptations such as:
1. Loss of unnecessary sense organs.
2. Loss of digestive system.
3. High reproductive capacity.
4. Presence of adhesive organs or suckers to cling on to the host.
Q7. Match the following and write correct choice in space provided.
| Animal | Characteristics | ||
| a. | Pila | (i) | Jointed appendages |
| b. | Cockroach | (ii) | Perching |
| c. | Asterias | . (iii) | Water vascular system |
| d. | Torpedo | (iv) | Electric organ |
| e. | Parrot | (v) | Presence of shell |
| f. | Dog fish | (vi) | Placoid scales |
Ans.
| Animal | . Characteristics | ||
| a. | Pila | (v) | Presence of shell |
| b. | Cockroach | (i) | Jointed appendages |
| c. | Asterias | (iii) | Water vascular system |
| d. | Torpedo | (iv) | Electric organ |
| e. | Parrot | (ii) | Perching |
| f. | Dog fish | (vi) | Placoid scales |
Q8. Differentiate between:
a. Open and closed circulatory system .
b. Oviparity and viviparity
c. Direct and indirect development
d. Aceolomate and pseudocoelomate
e. Notochord and nerve cord
f. Polyp and medusa
Ans: a. The circulatory system may be of two types:
1. Open type in which the blood is pumped out of the heart and the cells and tissues are directly bathed in it. E.g.: Arthropoda, Mollusca and Hemichordata.
2. Closed type in which the blood is circulated through a series of vessels of varying diameters (arteries, veins and capillaries). E.g.: Annelida and Chordata.
b. Oviparous animals give birth to an egg while viviparous animals are those that give birth to the live young ones.
c. Direct development: It is a type of development in which an embryo develops into a mature individual without involving a larval stage. Indirect development: It is a type of development that involves a sexually-immature larval stage.
d. Acoelomate: The animals in which the body cavity is absent are •called acoelomates, e.g.: Porifers, Coelentrates, Ctenophores and Platyhelminthes. ,
Pseudocoelomate: In some animals, the body cavity is not lined by mesoderm, instead, the mesoderm is present as scattered pouches in between the ectodenp and endoderm. E.g., aschelminthes
e. Notochord is a mesodermally derived rod-like-structure formed on the
dorsal side during embryonic development in some animals and it is the part of skeletal system. .
Nerve cord is the part of nervous system.
f. The polyp is a sessile and cylindrical fonn like Hydra, Adamsia, etc., whereas, the medusa is umbrella-shaped and free-swimming like Aurelia or jelly fish.
Q9. Give the characteristic features of the following citing one example of each:
a. Chondrichthyes and osteichthyes
b. Urochordata and cephalochordata
Ans: a. Chondrichthyes-. They are marine animals with streamlined body and have cartilaginous endoskeleton. Mouth is located ventrally. Notochord is persistent throughout life. Gill slits are separate and without operculum (gill cover). The skin is tough, containing minute placoid scales. Teeth are modified placoid scales which are backwardly directed. Their jaws are very powerful. These animals are predaceous. Due to the absence of air bladder, they have to swim constantly to avoid sinking. Scoliodon (Dog fish), Pristis (Saw fish), Carcharodon (Great white shark), Trygon (Sting ray).
Osteichthyes: It includes both marine and fresh water fishes with bony endoskeleton. Their body is streamlined. Mouth is mostly terminal. They have four pairs of gills which are covered by an operculum on each side. Skin is covered with cycloid/ctenoid scales. Air bladder is present which regulates buoyancy.
Examples: Marine—Exocoetus (Flying fish), Hippocampus (Sea horse); Freshwater—Labeo (Rohu), Catla (Katla), Clarias (Magur); Aquarium—Betta (Fighting fish), Pterophyllum (Angel fish),
b. Subphyla Urochordata and Cephalochordata are often referred to as protochordates and are exclusively marine. In Urochordata, notochord is present only in larval tail, while in Cephalochordata, it extends from head to tail region and is persistent throughout their life.
Examples: Urochordata—Ascidia, Salpa, Doliolum; Cephalochordata— Branchiostoma (Amphioxus or Lancelet).
Q10. Mention two similarities between:
Aves and mammals
A frog and crocodile ‘
A turtle and pila
Ans: Similarities between aves and mammalian
(i) Both are homeothermic animals (warm blooded)
(ii) Both have four chambered heart
b. Similarities between frog and crocodile
(i) Both are poikilothermic animals (cold blooded)
(ii) Both are oviparous animals
c. Similarities between turtle and Pila
(i) Both are poikilothermic animals (cold blooded)
(ii) Both are oviparous animals
Q11. Name
a. A limbless animal ‘
b. A cold blooded animal
c. A warm blooded animal
d. An animal possessing dry and comified skin
e. An animal having canal system and spicules
f. An animal with cnidoblasts
Ans: a. A limbless animal: Icthyophis
b. A cold blooded animal: Trygon (sting ray)
c. A warm blooded animal: Macaca (monkey)
d. An animal possessing dry and comifiedskin: Naja (Cobra)
e. An animal having canal system and spicules: Euspongia (bath sponge)
f. An animal with cnidoblasts: Hydra.
Q12. Give an example for each of the following:
a. A viviparous animal
b. A fish possessing a poison sting
c. A fish possessing an electric organ
d. An organ, which regulates buoyancy
e. Animal, which exhibits alternation of generation
f. Oviparous animal with mammary gland.
Ans: a. A viviparous animal: Panthera leo (lion)
b. A fish possessing a poison sting: Trygon (sting ray)
c. A fish possessing an electric organ: Torpedo
d. An organ, which regulates buoyancy: Air bladder
e. Animal, which exhibits alternation of generation: Obelia (Sea-fur)
f. Oviparous animal with mammary gland: Echidna (Platypus).
Q13. Excretory organs of different animals are given below. Choose correctly and write in the space provided.
| Animal | Excetory Organ/Unit | ||
| a. | Balanoglossus | (i) | Metanephridia |
| b. | Leech | (ii) | Nephridia |
| c. | Locust | (iii) | Flame cells |
| d. | Liver fluke | (iv) | Absent |
| e. | Sea urchin | (v) | Malpighian tubule |
| f. | Pila | (vi) | Proboscis gland |
Ans.
| a. | Balanoglossus | (vi) | Proboscis gland |
| b. | Leech | (ii) | Nephridia |
| c. | Locust | (v) | Malpighian tubule |
| d. | Liver fluke | (iii) | Flame cells |
| e. | Sea urchin | (iv) | Absent |
| f. | Pila | (0 | Metanephridia |
Long Answer Type Questions
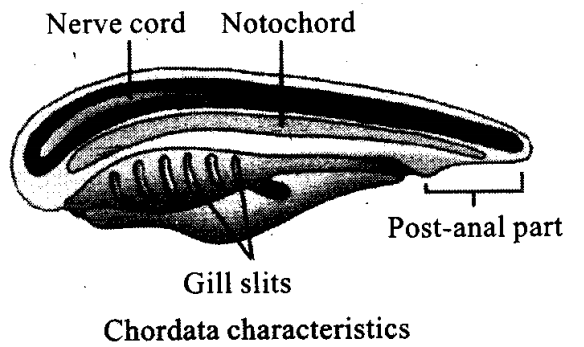
Q1. Give three major differences between chordates and non-chordates and draw a schematic sketch of a chordate showing those features.
Ans: Animals belonging to phylum Chordata are fundamentally characterised by the presence of a notochord, a dorsal hollow nerve cord and paired
pharyngeal gill slits. These are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, coelomate with organ-system level of organisation. They possess a post anal tail and a closed circulatory system.
| S. No. | Chordates | Non-chordates |
| 1. | Notochord present. | Notochord absent. |
| 2. | Central nervous system is dorsal, hollow and single. | Central nervous system is ventral, solid and double. |
| 3. | Pharynx perforated by gill slits. | Gill slits are absent. |
| 4. | Heart is ventral. | Heart is dorsal (if present). |
| 5. | A post-anal part (tail) is present. | Post-anal tail is absent. |
Q2. What is the relationship between germinal layers and the formation of body cavity in case of coelomate, acoelomates and pseudocoetomates?
Ans: Presence or absence of a cavity between the body wall and the gut wall is very important in classification. The body cavity, which is lined by mesoderm is called coelom. Animals possessing coelom are called coelomates, e.g., annelids, molluscs, arthropods, echinoderms, hemichordates and chordates. In some animals, the body cavity is not lined by mesoderm, instead, the mesoderm is present as scattered pouches in between the ectoderm and endoderm. Such a body cavity is called pseudocoelom and the animals possessing them are called pseudocoelomates, e.g., aschelminthes. The animals in which the body cavity is absent are called acoelomates, e.g., platyhelminthes
Q3. Comment upon the habitats and external features of animals belonging to class, amphibia and reptilia.
Ans: Class—Amphibia As the name indicates (Gr., Amphi: dual, bios, life), amphibians can live in aquatic as well as terrestrial habitats. Most of them have two pairs of limbs. Body is divisible into head and trunk. Tail may be present in some. The amphibian skin is moist (without scales). The eyes have eyelids. A tympanum represents the ear.
Examples: Bufo (Toad), Rana (Frog), Hyla (Tree frog), Salamandra (Salamander), Ichthyophis (Limbless amphibia).
Class-Reptilia :The class name refers to their creeping or crawling mode of locomotion (Latin, repere or reptum, to creep or crawl). They are mostly terrestrial animals and their body is covered by dry and comified skin, epidermal scales or scutes. They do not have external ear openings. Tympanum represents ear. Limbs, when present, are two pairs.
Examples: Chelone (Turtle), Testudo (Tortoise), Chameleon (Tree lizard), Calotes (Garden lizard), Crocodilus (Crocodile), Alligator (Alligator). Hemidactylus (Wall lizard), Poisonous snakes – Naja (Cobra), Bangarus (Krait), Vipera (Viper).
Q4. Mammals are most adapted among the vertebrates. Elaborate.
Ans: Mammals are most adapted among the vertebrates as they are found in a variety of habitats – polar ice caps, deserts, mountains, forests, grasslands and*dark caves. Some of them have adapted to fly or live in water.
They have two pairs of limbs, adapted for walking, running, climbing,. burrowing, swimming or flying. The skin of mammals is unique in possessing hair. External ears or pinnae are present. Different types of teeth are present in the jaw. Heart is four chambered.
They are ‘homoiot’hermous. Respiration is by lungs. Sexes are separate and fertilisation is internal. They are viviparous with few exceotions and development is direct.
NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Biology Solutions
- Chapter 1 The Living World
- Chapter 2 Biological Classification
- Chapter 3 Plant Kingdom
- Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom
- Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering Plants
- Chapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animals
- Chapter 8 Cell: The Unit of Life
- Chapter 9 Biomolecules
- Chapter 10 Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- Chapter 11 Transport in Plants
- Chapter 12 Mineral Nutrition
- Chapter 13 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
- Chapter 14 Respiration in Plants
- Chapter 15 Plant Growth and Development
- Chapter 16 Digestion and Absorption
- Chapter 17 Breathing and Exchange of Gases
- Chapter 18 Body Fluids and Circulation
- Chapter 19 Excretory Products and Their Elimination
- Chapter 20 Locomotion and Movement
- Chapter 21 Neural Control and Coordination
- Chapter 22 Chemical Coordination and Integration
NCERT Exemplar ProblemsMathsPhysicsChemistryBiology
We hope the NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.