Important Questions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 Important Questions
Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 Important Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
A solution of KOH hydrolyses CH3CHClCH2CH3 and CH3CH2CH2CH2Cl. Which one of these is more easily hydrolysed? (Delhi 2010)
Answer:
In aq. KOH SN1 mechanism takes place and the formed carbocation is stabilized. Thus 2° carbocation is more stable carbocation than 1° therefore
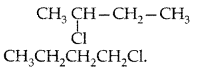
hydrolyses faster than CH3CH2CH2CH2Cl.
Question 2.
Give the IUPAC name of the following compound : (All India 2010)
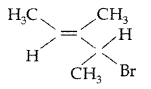
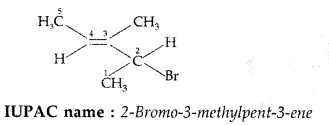
Answer:
Question 3.
Write the IUPAC name of the following compound : (CH3)3 CCH2Br (Delhi 2010)
Answer:
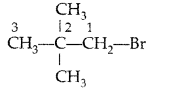
IUPAC name : 1-bromo-2, 2-dimethyl propane
Question 4.
Write the IUPAC name of the following compound : CH2 = CHCH2Br (All India 2010)
Answer:
![]()
IUPAC name : l-Bromo-prop-2-ene
Question 5.
Write the IUPAC name of the following compound : (All India 2010)
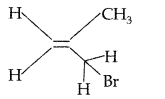
Answer:
IUPAC name : 1 -Bromo-2~methylprop-2-ene.
Question 6.
Give the IUPAC name of the following compound. (Delhi 2012)
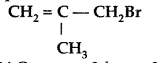
Answer:
IUPAC name : 3-bro?no-2-methyl propene
Question 7.
What happens when bromine attacks (All India 2012)
CH2 = CH – CH2 – C ≡ CH
Answer:
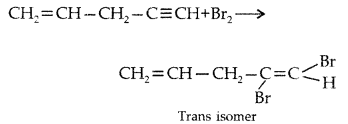
Question 8.
Write the IUPAC name of the following : (All India 2012)
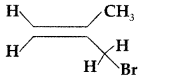
Answer:
IUPAC name : 3 Bromo-2-methyl propene.
Question 9.
Draw the structure of major monohalogen product formed in the following reaction : (Comptt. Delhi 2012)
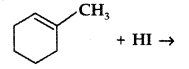
Answer:
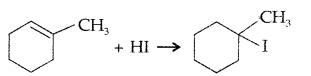
Question 10.
In the following pair of compounds, which will react faster by SN1 mechanism and why? (Comptt. Delhi 2012)
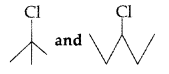
Answer:
![]()
reacts faster by SN1 mechanism as it is a tertiary halide and it produces a stable tertiary carbocation.
Question 11.
Draw the structure of major monohalogen product in the following reaction : (Comptt. Delhi 2012)
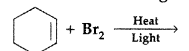
Answer:
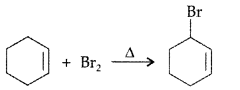
Question 12.
Predict the order of reactivity of four isomeric bromobutanes in SN1 reaction. (Comptt. Delhi 2012)
Answer:
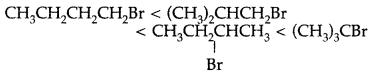
Question 13.
Predict the order of reactivity of the following compounds in SN1 reaction :
C6H5CH2Br, C6H5C(CH3) (C6H5)Br, C6H5CH(C6H5)Br, C6H5CH(CH3)Br (Comptt. Delhi 2012)
Answer:
C6H5C(CH3) (C6H5)Br > C6H5CH(C6H5)Br > C6H5CH(CH3)Br > C6H5CH2Br
Question 14.
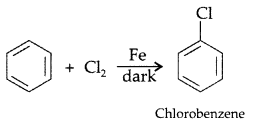
Draw the structure of major monohalogen product in the following reaction : (Comptt. Delhi 2012)
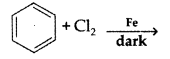
Answer:
Question 15.
Give a chemical test to distinguish between C2H5Br and C6H5Br. (Comptt. All India 2012)
Answer:
Both are heated with aqueous NaOH. C2H5Br gives ethanol and NaBr, which on reacting with AgNO3, gives yellow precipitate of AgBr.
C6H5Br does not respond to this test.
Question 16.
Arrange the following in increasing order of boiling point:
(i) CH3CH2CH2CH2Br
(ii) (CH3)3.Br
(iii) (CH3)2C.Br (Comptt. All India 2012)
Answer:
(CH3)2C.Br < (CH3)2.CHCH2.Br < CH3CH2CH2CH2Br
Question 17.
Write the IUPAC name of the following : (Comptt. All India 2012)
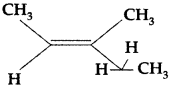
Answer:
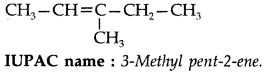
Question 18.
Write the IUPAC name of
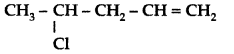 (Delhi 2013)
(Delhi 2013)
Answer:
IUPAC name : 4-chloropent-l-ene
Question 19.
What happens when CH3 — Br is treated with KCN? (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
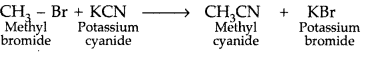
Question 20.
Write the IUPAC name of (Delhi 2013)
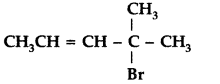
Answer:
IUPAC name : 4-bromo-4-methylpent-2-ene
Question 21.
What happens when ethyl chloride is treated with aqueous KOH? (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
![]()
Question 22.
Write the IUPAC name of (CH3)2CH.CH(Cl)CH3. (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
IUPAC name : 2-chloro-3-methylbutane
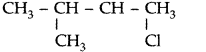
Question 23.
Which compound in the following pair undergoes faster SN1 reaction. (Delhi 2013)
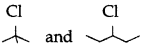
Answer:
![]()
reacts faster by SN1 mechanism as it is a tertiary halide and it produces a stable tertiary carbocation.
Question 24.
Write the IUPAC name of the following compound: (All India 2013)
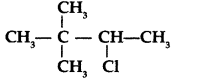
Answer:
IUPAC name : 2-Chloro-3, 3-dimethylbutane.
Question 25.
Write the IUPAC name of the following compound : (All India 2013)
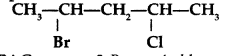
Answer:
IUPAC name : 2-Bromo-4-chloropentane
Question 26.
Write the IUPAC name of the following compound : (All India 2013)
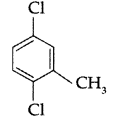
Answer:
IUPAC name : 2, 5-dichlorotoluene
Question 27.
In the following pair of halogen compounds, which compound will react faster by SN1 mechanism? (Comptt. Delhi 2013)
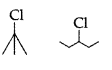
Answer:

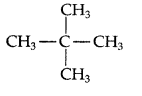
Question 28.
A hydrocarbon C5H12 gives only one mono-chlorination product. Identify the hydrocarbon. (Comptt. Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Since there is only one monochloroderivative, the compound contains 12 equivalent hydrogen in four equivalent CH3. The compound is 2, 2-dimethyl propane
Question 29.
Identify the chiral molecule in the following pair : (All India 2014)
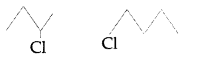
Answer:
(2-Chlorobutane) is a chiral molecule.
Question 30.
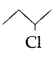
Draw the structure of 2-bromopentane. (Comptt. Delhi 2014)
Answer:
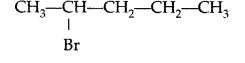
Question 31.
Which would undergo SN2 reaction faster in the following pair and why? (Delhi 2015)
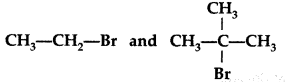
Answer:
CH3CH2Br reacts faster because it is a primary halide (1° halide).
Question 32.
Which would undergo SN1 reaction faster in the following pair : (All India 2015)
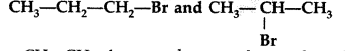
Answer:
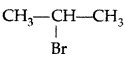
because the secondary carbocation formed is more stable than primary carbocation.
Question 33.
Out of

which is more reactive towards SN1 reaction and why? (Delhi 2016)
Answer:

Question 34.
Write the structure of an isomer of compound C4H9Br which is most reactive towards SN1 reaction. (All India 2016)
CH3
Answer:
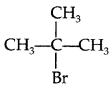
(2-Bromo-2-methyl propane) or tert-butyl bromide is most reactive towards SN1 reaction as it Br can form 3° carbocation.
Question 35.
Write the structure of l-Bromo-4-chlorobut-2-ene. (Delhi 2017)
Answer:
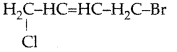
Question 36.
Write the structure of 2, 4-dinitrochlorobenzene. (Delhi 2017)
Answer:
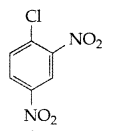
Question 37.
Out of
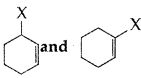 which is an example of allylic halide? (All India 2017)
which is an example of allylic halide? (All India 2017)
Answer:

Question 38.
Out of
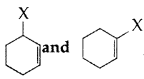 which is an example of vinylic halide? (All India 2017)
which is an example of vinylic halide? (All India 2017)
Answer:
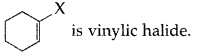
Question 39.
Out of
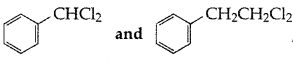
which is an example of a benzylic halide? (All India 2017)
Answer:
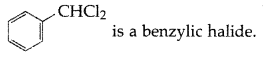
Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 Important Questions Short Answer Type -I [SA – I]
Question 40.
Which one in the following pairs of substances undergoes SN2 substitution reaction faster and why? (Delhi 2009)
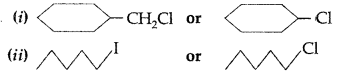
Answer:
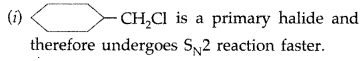

Question 41.
Which one in the following pairs undergoes SN1 substitution reaction faster and why? (All India 2009)
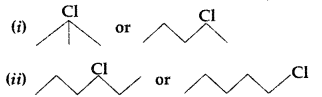
Answer:
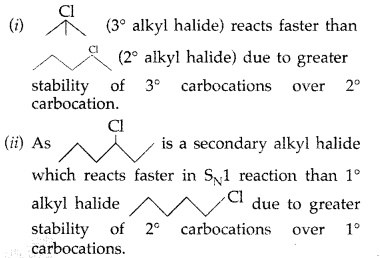
Question 42.
Complete the following reaction equations : (All India 2009)
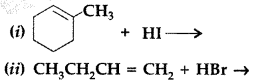
Answer:
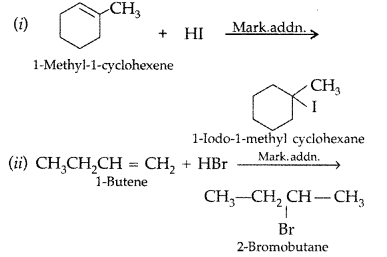
Question 43.
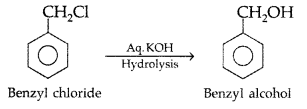
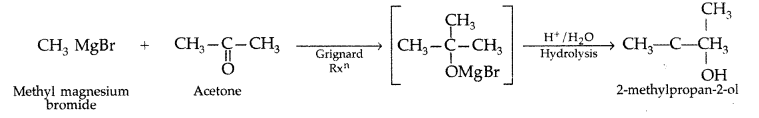
How are the following conversions carried out?
(i) Benzyl chloride to benzyl alcohol,
(ii) Methyl magnesium bromide to 2-methyl- propan-2-ol. (Delhi 2010)
Answer:
(i) Benzyl chloride to benzyl alcohol
(ii) Methyl magnesium bromide to 2-methylpropan-2-ol
Question 44.
Haloalkanes undergo nucleophilic substitution whereas haloarenes undergo electrophilic substitution. Explain. (Comptt. Delhi 2012)
Answer:
Haloarenes (say chlorobenzene) is a resonance hybrid of the following five structures :
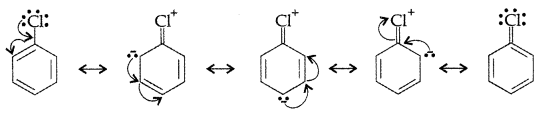
Resonance leads to lowering of energy and hence greater stability. On the other hand, no such resonance is possible in haloalkanes. Halogens directly attached to benzene ring are o, p-directing in electrophilic subsitution reactions. This is due to greater electron density at these positions in resonance.
Question 45.
Chlorobenzene is extremely less reactive towards a nucleophilic substitution reaction. Give two reasons for the same. (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
The reasons are:
(i) Due to resonance/diagrammatic repre-sentation, C – Cl bond acquires a partial double bond character. As a result, the C – Cl bond in chlorobenzene is shorter and hence stronger. Thus, cleavage of C – Cl bond in benzene becomes difficult which makes it less reactive towards nucleophilic substition.
(ii) Due to repulsion between nucleophile and electron rich arenes.
Question 46.
(a) Why does p-dichlorobenzene have a higher m.p. than its o- and m-isomers?
(b) Why is (±)-Butan-2-ol optically inactive? (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
(a) p-isomers are comparetively more symmetrical and fit closely in the crystal lattice, thus require more heat to break these strong forces of attraction. Therefore higher melting point than o- and m-isomers.
(b) (±)-Butan-2-ol is optically inactive because in racemic mix one type of rotation is cancelled by other.
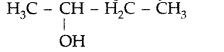
Question 47.
Account for the following:
(i) The C – Cl bond length in chlorobenzene is shorter than that in CH3 – Cl.
(ii) Chloroform is stored in closed dark brown bottles. (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
(i) In haloalkanes, the halogen atom is attached
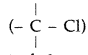
to sp3-hybridized carbon while in haloarenes it is attached to sp2 -hybridized carbon whose size is smaller than sp3 orbital carbon. Therefore C – Cl bond in chloro-benzene is shorter than alkyl chloride.
(ii) CHCl3 is stored in dark coloured bottles to cut off light because CHCl3is slowly oxidised by air in presence of light to form an extremely poisonous gas, carbonyl chloride, popularly known as phosgene.
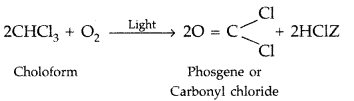
Question 48.
Give chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds :
(a) Benzyl chloride and Chlorobenzene
(b) Chloroform and Carbon tetrachloride (Comptt. Delhi 2013)
Answer:
(a) Chlorobenzene and Benzyl chloride :
Benzyl chloride is more reactive than chlorobenzene towards nucleophillic substitution reactions, therefore, benzyl chloride on boiling with aqueous KOH produces benzyl alcohol and KCl.
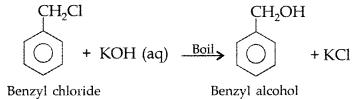
The reaction mixture on acidification with dil. HNO3 followed by treatment with AgNO3 solution produces white ppt. of AgCl due to formation of KCl
![]()
But chlorobenzene does not undergo hydrolysis under these mild conditions to give phenol and KCl.
(b) Chloroform and Carbon tetrachloride
By Carbylamine test: CCl4 does not give this reaction but chloroform gives this reaction and produces offensive smell of phenyl isocyanide.
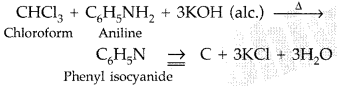
Question 49.
Explain why :
(a) The dipole moment of chlorobenzene is lower than that of cyclohexyl chloride.
(b) Alkyl halides, though polar, are immiscible with water. (Comptt. All India 2013)
Answer:
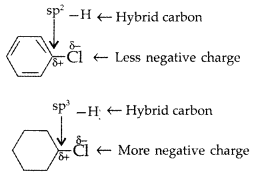
(a) Chlorobenzene has lower dipole moment than cyclohexyl chloride due to lower magnitude of -ve charge on the Cl atom and shorter C – Cl distance. Due to greater S-character, a sp2-hybrid carbon is more electronegative than a sp3-hybrid carbon. Therefore, the sp2-hybrid carbon of C – Cl bond in chlorobenzene has less tendency to release electrons to Cl than a sp3 hybrid carbon of cyclohexyl chloride.
(b) Alkyl halides and polar molecules are held together by dipole-dipole interaction. The molecules of H2O are held together by H- bonds. Since the new forces of attraction between water and alkyl halide molecules are weaker than the forces of attraction already existing between alkyl halide-alkyl halide molecules and water-water molecules, therefore alkyl halides are immiscible (not soluble) with water.
Question 50.
(i) Which alkyl halide from the following pair is chiral and undergoes faster SN2 reaction?
(ii) Out of SN1 and SN2, which reaction occurs with
(a) Inversion of configuration
(b) Racemisation (Delhi 2014)
Answer:

(ii) (a) Inversion of configuration occurs with SN2 reaction.
(b) Racemisation occurs with SN1 reaction.
Question 51.
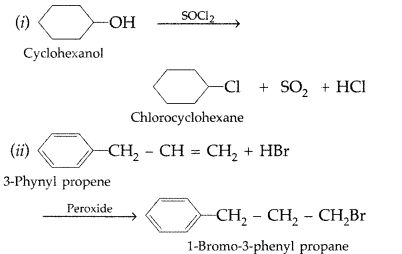
Draw the structure of major monohalo product in each of the following reactions : (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
Question 52.
Write the IUPAC names of the following compounds :
(i) CH2 = CHCH2Br
(ii) (CCl3)3 CCl (Comptt. All India 2014)
Answer:
(i) CH2 = CHCH2 – Br
IUPAC name : 3-Bromopropene
(ii) (CCl3)2—C—Cl :
IUPAC name : 2-(Trichloromethyl) – 1, 1, 1, 2, 3, 3, 3-heptachloropropane
Question 53.
What are ambident nucleophiles? Explain with an example. (Comptt. All India 2014)
Answer:
Ambident nucleophile : A nucleophile that can form new bonds at two or more spots in its structure, usually due to resonance contributors. Example: S = C = N– can act as a nucleophile with either the S or N attacking.
Question 54.
Write the structures of the following organic halogen compounds :
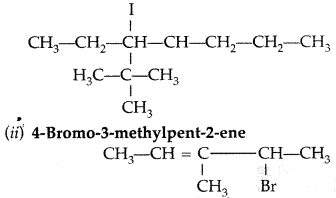
(i) 4-tert-Butyl-3-iodoheptane
(ii) 4-Bromo-3-methylpent-2-ene (Comptt. All India 2014)
Answer:
(i) 4-tert-Butyl-3-iodoheptane
Question 55.
Write the structures of the following organic halogen compounds :
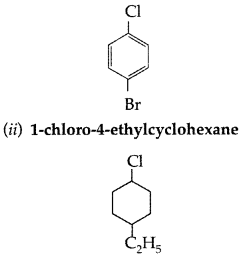
(i) p-Bromochlorobenzene
(ii) 1-Chloro-4-ethylcyclohexane (Comptt. All India 2014)
Answer:
(i) p-Bromochlorobenzene
Question 56.
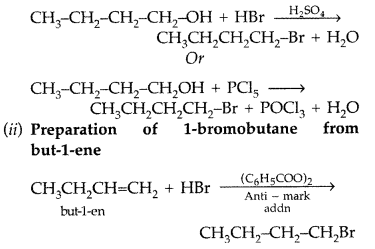
Write the equations for the preparation of 1-bromobutane from :
(i) 1-butanol (ii) but-l-ene (Comptt. All India 2016)
Answer:
(i) Preparation of 1-bromobutane from 1-butanol
Question 57.
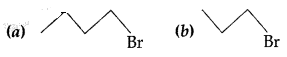
Which compound in each of the following pairs will react faster in SN2 reaction with —OH?
(i) CH3Br or CH3I (ii) (CH3)3 CCl or CH3Cl (Comptt. All India 2016)
Answer:
(i) CH3I: Because Iodide is better leaving group than bromide.
(ii) CH3Cl : Carbon atom leaving group is less hindered.
Question 58.
Which alkyl halide from the following pair is (i) Chiral and (ii) undergoes SN2 reaction faster? (Comptt. Delhi 2017)
Answer:

Question 59.
Which alkyl halide from the following pair is (i) Chiral and (ii) undergoes SN1 reaction faster?
(a) (CH3)2CBr
(b) CH3CH2CHBrCH3 (Comptt. Delhi 2017)
Answer:
(i) 2-Bromobutane is chiral as the central C atom has all 4-different groups.
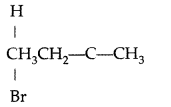
(ii) 3° Alkyl bromide i.e. (CH3)3CBr undergoes SN1 reaction faster due to more stability of 3° carbocation.
Question 60.
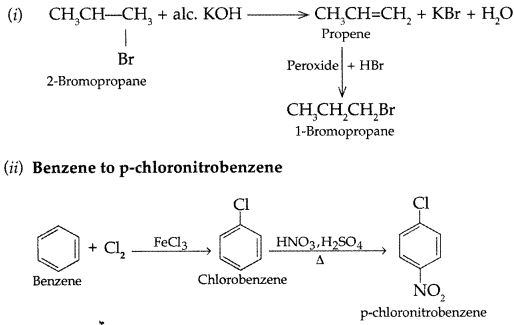
How will you carry out the following conversions :
(i) 2-Bromopropane to 1-bromopropane
(ii) Benzene to p-chloronitrobenzene
Answer:
Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 Important Questions Short Answer Type -II [SA – II]
Question 61.
(i) State one use each of DDT and iodoform.
(ii) Which compound in the following couples will react faster in SN2 displacement and why?
(a) 1-bromopentane or 2-bromopentane
(b) l-bromo-2-methylbutane or 2-bromo-2-methylbutane. (Delhi 2010)
Answer:
(i) Use of DDT (Dichlorodiphenyl Trichloroethane): As a powerful insecticide, it is widely used for sugarcane and fodder crops to kill mosquitoes, lice which carry pathogens.
Use of iodoform (CHI3) : It is used as an antiseptic for dressing wounds. Its antiseptic action is due to liberation of iodine when iodoform comes in contact with skin but not due to iodoform itself.
(ii) In SN2 reactions, reactivity depends upon steric hindrance
(a) 1-Bromopentane (1° halogen) having less steric hindrance therefore is more reactive than 2-Bromopentane hence undergoes SN2 reactions faster.
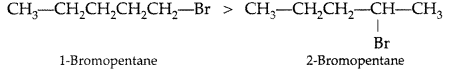
(b) 1-Bromo-2-methylbutane having less steric hindrance, is thus more reactive towards SN2 reaction than 2-bromo-2-methyl butane (more steric hindrance).
Question 62.
How would you differentiate between S<subN1 and SN2 mechanisms of substitution reactions? Give one example of each. (All India 2010)
Answer:
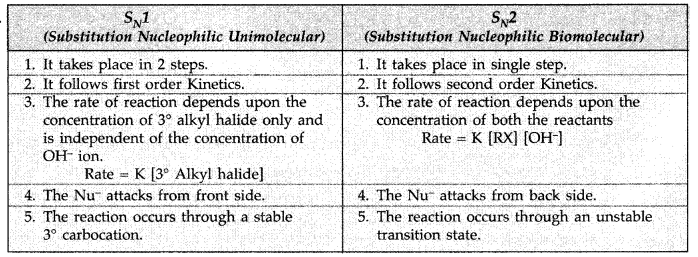
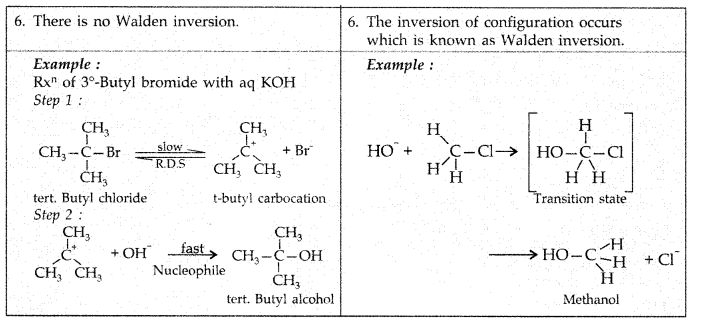
Question 63.
Answer the following :
(i) Haloalkanes easily dissolve in organic solvents, why?
(ii) What is known as a racemic mixture? Give an example.
(iii) Of the two bromoderivatives, C6H5CH (CH3)Br and C6H5CH(C6H5)Br, which one is more reactive in SN1 substitution reaction and why? (Delhi 2011)
Answer:
(i) Because the new forces of attraction set up between haloalkanes and solvent molecules are of the same strength as the forces of attraction being broken.
(ii) A mixture which contains the equal proportions of two enantiomers of a compound in equal proportions is called racemic mixture
Example : (±) butan-2-ol
(iii) Since the reactivity of SN1 reactions increases as the stability of intermediate carbocation increases. Of the two 2° bromides, the carbocation intermediate derived from C6H-CH(C6H5)Br i.e. C6H5CHC6H5 is more stable as compared to the carbocation (mathrm{C}_{6} mathrm{H}_{5}^{+} mathrm{CHCH}_{3}) obtained from C6H5CH(CH3)Br because it is stabilized by two phenyl groups due to resonance.
Question 64.
Rearrange the compounds of each of the following sets in order of reactivity towards SN2 displacement :
(i) 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 1-Bromopentane, 2-Bromopentane
(ii) l-Bromo-3-methylbutane, 2-Bromo-2-methyl-butane, 3-Bromo-2-methylbutane
(iii) 1-Bromobutane, l-Bromo-2,2-dimethyl-propane, l-Bromo-2-methylbutane (All India 2011)
Answer:
(i) 1-Bromopentane > 2-Bromopentane > 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane
(ii) 1-Bromo-3-methylbutane > 3-Bromo-2 methylbutane > 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane
(iii) 1-Bromobutane > 1-Bromo-2-methylbutane > 1-Bromo-2, 2-dimethylpropane.
Question 65.
Although chlorine is an electron withdrawing group, yet it is ortho-, para-directing in electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions. Explain why it is so? (Delhi 2012)
Answer:
Chlorine withdraws electrons through inductive effect and releases through resonance. Although Cl shows -1 effect but through resonance, Cl tends to stabilize the intermediate carbocation and the effect is more pronounced at ortho and para positions.
This can also be explained diagramatically as:
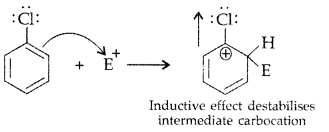
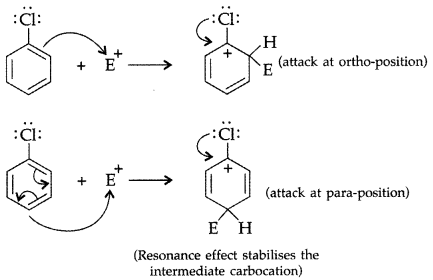
Question 66.
Answer the following questions : (All India 2012)
(i) What is meant by chirality of a compound? Give an example.
(ii) Which one of the following compounds is more easily hydrolyzed by KOH and why?
CH3CHClCH2CH3 or CH3CH2CH2Cl
(iii) Which one undergoes SN2 substitution reaction faster and why?
![]()
Answer:
(i) Chirality : The objects which are non-superimposable on their mirror image are said to be chiral and this property is known as chirality for Butan-2-ol
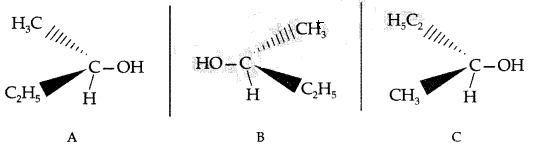
C is non-superimposable on its mirror image A.

(iii) As I is a better leaving group because of its large size, it will be released at a faster rate in the presence of incoming nucleophile.
![]()
Question 67.
Account for the following :
(a) The dipole moment of chlorobenzene is lower than that of cyclohexyl chloride.
(b) Alkyl halides, though polar, are immiscible with water.
(c) Grignard’s reagents should be prepared under anhydrous conditions. (Comptt. All India 2012)
Answer:
(a) Electron pairs of Cl atom are in conjugation with n electrons of the benzene ring so C-Cl bond in chlorobenzene
acquires some double bond character while C-Cl bond in cyclohexyl chloride is a pure single bond.
C – Cl bond in chlorobenzene is shorter than in cyclohexyl chloride. Since dipole moment is a product of charge and distance, so chlorobenzene has lower dipole moment than cyclohexyl chloride.
(b) Alkyl halides are polar molecules, therefore, their molecules are held together by dipole-dipole attraction. The molecules of H2O are held together by H-bonds. Since the new forces of attraction between water and alkyl halide molecules are weaker than the forces of attraction already existing between alkyl halide- alkyl halide molecules and water- water molecules, therefore, alkyl halides are immiscible with water.
(c) Grignard’s reagents are very reactive. They react with alcohol, water, amines etc. to form corresponding hydrocarbon.
R-MgX + HOH → RH + Mg(OH)X
Therefore, Grignard’s reagents must be prepared under anhydrous conditions.
Question 68.
Give reasons for the following :
(i) Ethyl iodide undergoes SN2 reaction faster than ethyl bromide.
(ii) (±) 2-Butanol is optically inactive.
(iii) C—X bond length in halobenzene is smaller than C—X bond length in CH3—X. (All India 2013)
Answer:
(i) I, is better leaving group/C—I bond is weaker than C—Br bond.
(ii) (±)-Butan-2-ol is optically inactive because in racemic mix one type of rotation is cancelled by other.
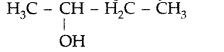
(iii) In halobenzene, halogen atom is attached to the sp2 hybrid carbon atom while in CH3-X halogen atom is attached to sp3 hybrid carbon atom. Hence C-X bond length in halo benzene is smaller than CH3-X.
Question 69.
(a) Draw the structures of major monohalo products in each of the following reactions :
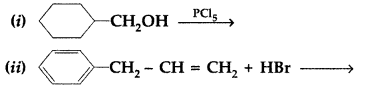
(b) Which halogen compound in each of the following pairs will react faster in SN2 reaction :
(i) CH3Br or CH3I
(ii) (CH3)3 C – Cl or CH3 – Cl (All India 2014)
Answer:
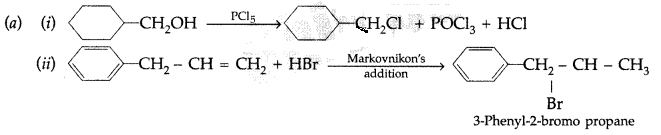
(b) (i) CH3Br will react faster in SN2 reaction.
(ii) CH3 – Cl will react faster in SN2 reaction.
Question 70.
(a) Which compound in each of the following pairs will react faster in SN2 reaction with -OH group?
(i) CH3Br or CH3I
(ii) (CH3)3CCl or CH3Cl
(b) Write the product of the following reactions: (Comptt. Delhi 2014)
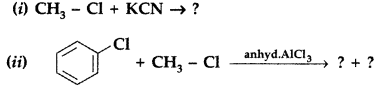
Answer:
(a) (i) As I– ion is a good leaning group than Br, therefore reacts faster than CH3Br in SN2 reactions with -OH.
(ii) As 3° alkyl halides have more steric hindrance than 1° alkyl halide therefore CH3Cl undergoes SN2 reaction faster than 3° alkyl
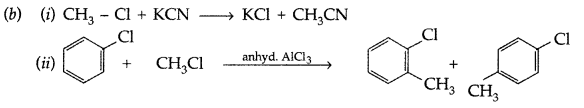
Question 71.
Give reasons :
(a) n-Butyl bromide has higher boiling point than f-butyl bromide.
(b) Racemic mixture is optically inactive.
(c) The presence of nitro group (-NO2) at o/p positions increases the reactivity of haloarenes towards nucleophilic substitution reactions. (Delhi 2015)
Answer:
(a) n-Butyl bromide has higher boiling point than f-butyl bromide because it has larger surface area hence have more Van der Waals’ forces.
(b) Rotation due to one enantiomer is cancelled by another enantiomer.
(c) The presence of nitro group (-NO2) at ortho and para positions withdraws the electron density’ from benzene ring and thus facilitating the attack of nucleophile.
Question 72.
How can the following conversions be carried out :
(i) Aniline to bromobenzene
(ii) Chlorobenzene to 2-chloroacetophenone
(iii) Chloroethane to butane (All India 2015)
Answer:
(i) Aniline to bromobenzene
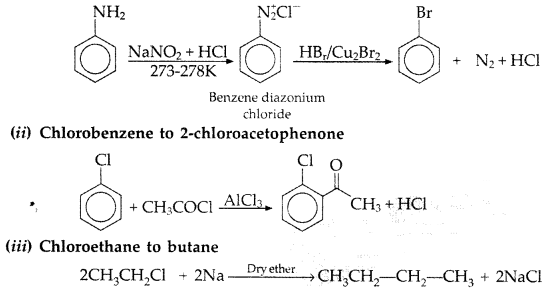
Question 73.
What happens when
(i) Chlorobenzene is treated with Cl2/FeCl3,
(ii) Ethyl chloride is treated with AgNO2,
(iii) 2-bromopentane is treated with alcoholic KOH?
Write the chemical equations in support of your answer. (All India 2015)
Answer:
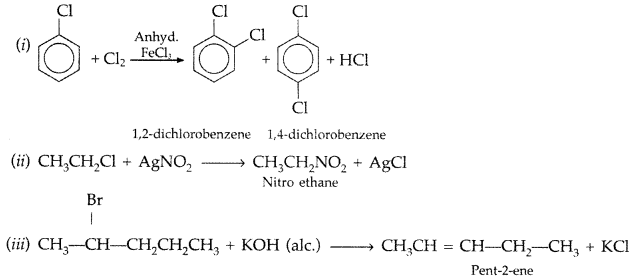
Question 74.
Name the following according to IUPAC system : (Comptt. Delhi 2015)

Answer:
(i) 2-Bromotoluene
(ii) 1 chloro, 2, 2 dimethyl propane
Question 75.
Give the IUPAC names of the following compounds : (Comptt. All India 2015)
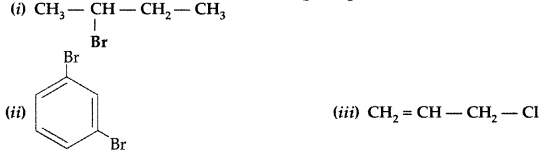
Answer:

Question 76.
Give reasons: (Delhi 2016)
(i) C—Cl bond length in chlorobenzene is shorter than C—Cl bond length in CH3—Cl.
(ii) The dipole moment of chlorobenzene is lower than that of cyclohexyl chloride.
(iii) SN1 reactions are accompanied by racemization in optically active alkyl halides.
Answer:
(i) In haloalkanes, the halogen atom is attached
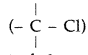
to sp3-hybridized carbon while in haloarenes it is attached to sp2 -hybridized carbon whose size is smaller than sp3 orbital carbon. Therefore C – Cl bond in chloro-benzene is shorter than alkyl chloride.
(ii) Dipole moment is the product of charge and inter nuclear distance. In case of cyclohexyl chloride carbon—chlorine band length is longer than C—Cl band length in chlorobenzene. Hence dipole moments of cyclohexyl chloride is more.
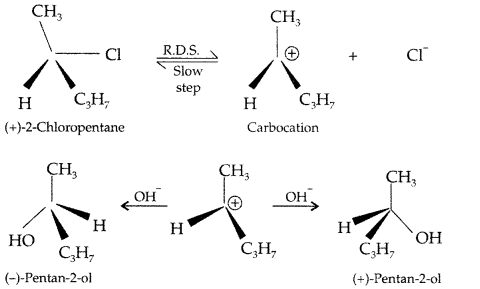
(iii) SN1 reactions are accompanied by racemization in optically active alkyl halides because the nucleophile will have an equal opportunity to attack on sp2 hybridised carbocation from either sides to give a racemic mixture.
Example:
Question 77.
How do you convert: (All India 2016)
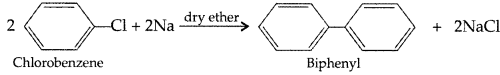
(i) Chlorobenzene to biphenyl
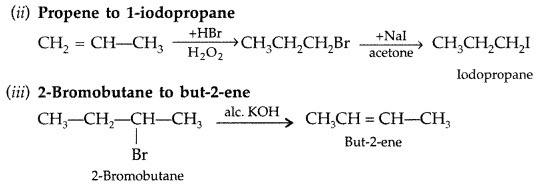
(ii) Propene to 1-iodopropane
(iii) 2-bromobutane to but-2-ene
Answer:
(i) Chlorobenzene to biphenyl (Fittig reaction)
Question 78.
Write the major product(s) in the following: (All India 2016)
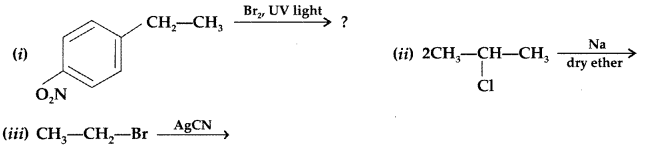
Answer:
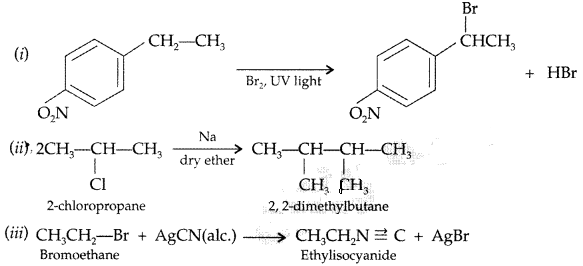
Question 79.
In the following pairs of the halogen compounds which compound undergoes faster SN1 reaction. (Comptt. Delhi 2016)
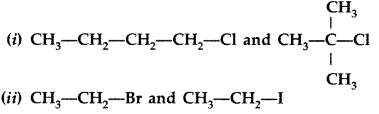
Answer:

Question 80.
What happens when
(i) CH3—Cl is treated with aqueous KOH?
(ii) CH3—Cl is treated with KCN?
(iii) CH3—Br is treated with Mg in the presence of dry ether? (Comptt. All India 2016)
Answer:
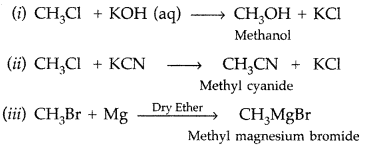
Question 81.
Following compounds are given to you:
2-Bromopentane, 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 1-Bromopentane
(i) Write the compound which is most reactive towards SN2 reaction.
(ii) Write the compound which is optically active.
(iii) Write the compound which is most reactive towards β – elimination reaction. (Delhi 2017)
Answer:
(i) 1-Bromopentane is most reactive towards SN2 reaction.
(ii) 2-Bromopentane is optically active.
(iii) 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane is most reactive towards β -elimination reaction.
Question 82.
Write structures of compounds A, B and C in each of the following reactions: (Delhi 2017)
![]() >
>
Answer:
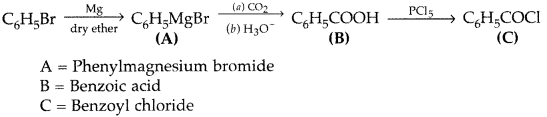
Question 83.
The following compounds are given to you:
2-Bromopentane, 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 1-Bromopentane
(i) Write the compound which is most reactive towards SN2 reaction.
(ii) Write the compound which is optically active.
(iii) Write the compound which is most reactive towards P-elimination reaction. (All India 2017)
Answer:
(i) 1-Bromopentane CH3CH2CH2CH2Br is most reactive towards SN2 reaction.
Question 84.
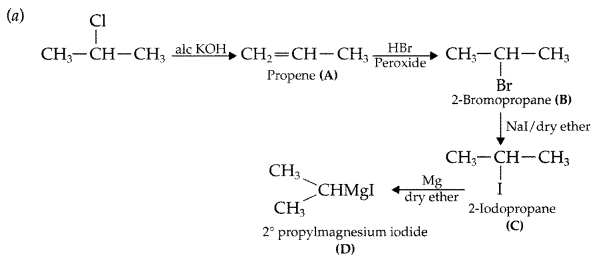
(a) Write the structural formula of A, B, C and D in the following sequence of reaction:
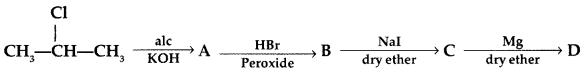
(b) Illustrate Sandmeyer’s reaction with the help of a suitable example. (Comptt. Delhi 2017)
Answer:
(b) Sandmeyer’s reaction: The substitution of diazo group of benzene diazonium chloride by Chloro, Bromo and Cyano group with the help of solution of CuCl dissolved in HC1, CuBr/HBr and CuCN/KCN respectively is known as Sandmeyer’s reaction.
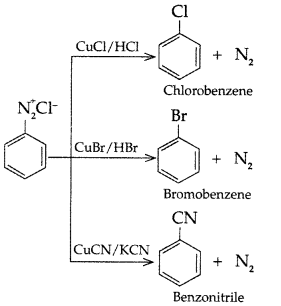
Question 85.
(a) Account for the following :
(i) Electrophilic substitution reactions in haloarenes occur slowly.
(ii) Haloalkanes, though polar, are insoluble in water.
(b) Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of reactivity towards SN2 displacement:
2-Bromo-2-Methylbutane, 1-Bromopentane, 2-Bromopentane (Comptt. All India 2017)
Answer:
(a) (i) Due to -I effect of halogen atom, it withdraws electrons from the benzene ring and thus ring gets deactivated.
(ii) They fail to form hydrogen bonds with water. More energy is required to break hydrogen bonds in water and less energy is released when new attractions are set up.
(b) 2-Bromo-2-Methylbutane < 2-Bromopentane < 1-Bromopentane
Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 Important Questions long Answer Type [LA]
Question 86.
(i) o-nitrophenol has lower b.p. than p-nitro-phenol. Explain.
(ii) Write IUPAC name of the following : (Comptt. Delhi 2013)
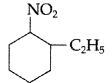
Answer:
(i) Ortho-nitrophenol has lower boiling point due to formation of intramolecular H-bonding whereas p-nitrophenol forms intermolecular H-bonding.
(ii) IUPAC name : 2-ethyl-l-nitrocyclohexane.
Important Questions for Class 12 Chemistry
<!–
–>