CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Solved 2016 Set 1
Section A
1 .State boiling point elevation constant for a solvent
2.What is denatured alcohol?
3.Explain why alkylamine is more basic than ammonia?
4.Write the IUPAC names of the following:
(i)Ethylidene chloride
(ii)Ethylene dichloride
5. How will you bring out the following conversion?
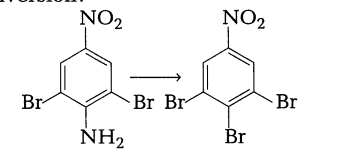
Section B
6.An aqueous solution containing 28% by mass of liquid A (molecular mass = 140) has a vapour pressure of 160 mm at 30°C. Find the vapour pressure of the pure liquid A (the vapour pressure of water at 30° C is 150 mm).
7.Define the following terms in relation to crystalline solids.
(i)Unit cell
(ii)Coordination number
Give one example of each case.
Or
The edge length of unit cell of a metal (molecular weight =24) having cubic structure is 4.53 A. If the density of metal is 1.74 gem-3 , the radius of metal is (Na =6 x 1023 ).
8.Chromium metal crystallises in a body centred cubic lattice. The length of the unit cell edge is found to be 287 pm. Calculate the atomic radius of chromium.
9.The standard oxidation potential of Ni/Ni2+ electrode is 0.236 V If this is combined with a hydrogen electrode in an acidic solution, at what pH of the solution will measured EMF be zero at 25°C? [Assuming [Ni2+ ] = 1M]
10.(i)(a) Give the reaction when KMnO4 reacts with H2 S in neutral medium.
(b) Reaction of KMn04 with S02 in acidic medium.
(ii) Why the highest oxidation state of a metal exhibited in its oxide or fluoride form only?
Section C
11.(i)Out of Cu2Cl2 and CuCl2, which is more stable? Why?
(ii) While filling up of electrons in the atomic orbitals, the 4s-orbital is filled before the 3d-orbital but reverse happens during the ionisation of the atom. Explain.
12.(i) NCI3 is an endothermic compound while, NF3 is an exothermic one. Explain.
(ii) (a) Applying VSEPR theory, draw the probable structure of SF4.
(b) Why SF6 is kinetically an inert substance?
13.(i) Define mutarotation and give one example.
(ii) The two strands of DNA are not identical but are complementary? Explain
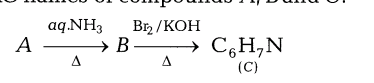
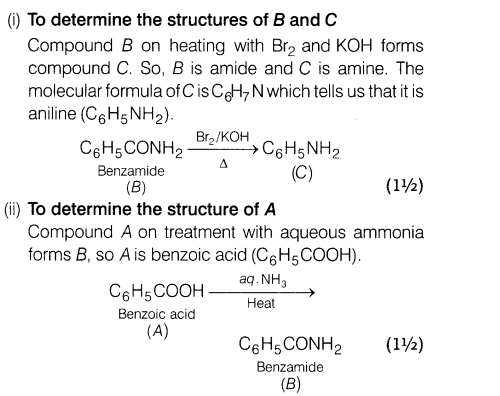
14.An aromatic compound A on treatment with aqueous ammonia and heating forms compound B which on heating with Br2 and KOH forms a compound C of molecular formula C6H7 Write the structures and IUPAC names of compounds A, Band C.
15.Explain the cleansing action of soaps.
Or
(i)How will you define an antacid?
(ii)Name a broad spectrum antibiotic and state two diseases for which it is prescribed.
16.Explain the formation of Helmholtz electrical double layer.
17.Explain a process in which a biocatalyst is used in industrial preparation of a compound
18.(i) Write the IUPAC name of the following molecules.
(a)K3[Co(N03)6]
(b)[Co(NH3)5ONO]2+
(ii) What is meant by bidentate and ambidentate ligands? Give two examples of each.
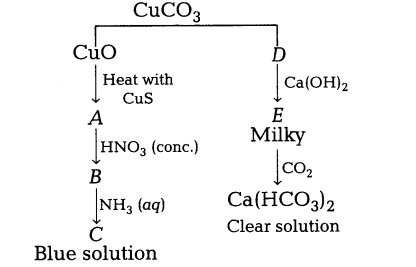
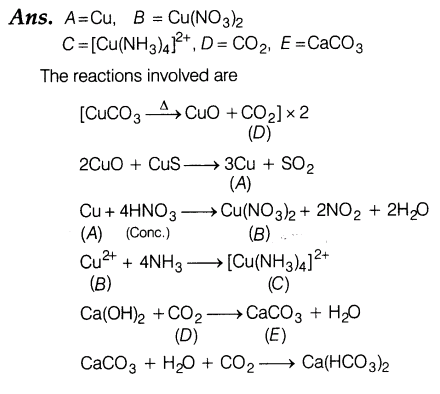
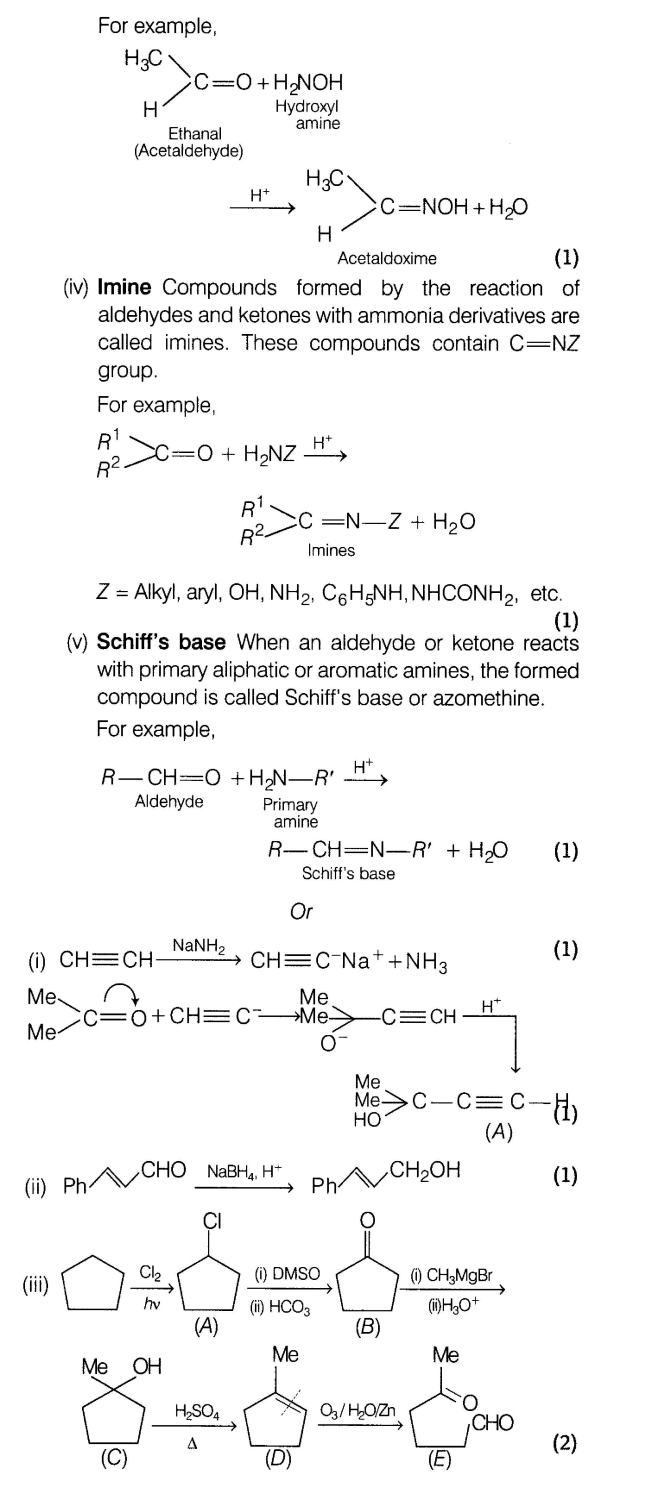
19.Identify A to E and also explain the reactions involved.
20.(i) The conductivity of 0.20 M solution of KC1 at 298 K is 0.0248 S cm-1 . Calculate its molar conductivity.
(ii) Amongst the fuel cells, H2— 02 fuel cell is most commonly used for providing electrical power in Apollo space programme. The cell runs continuously as long as the reactants are supplied.
Write the reactions occurring at cathode and anode.
21.(i) Write the preparation of neoprene.
(ii) What is a biodegradable polymer? Give an example of a biodegradable aliphatic polyester (with reaction).
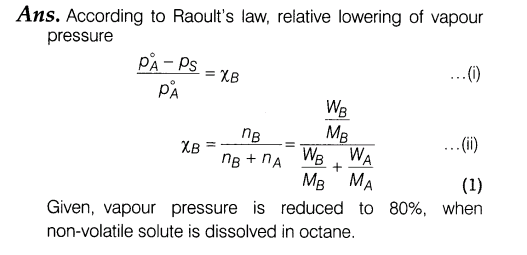
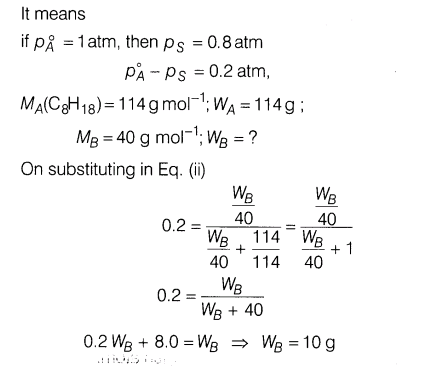
22.Calculate the mass of a non-volatile solute (molar mass = 40 g mol-1) which should be dissolved in 114 g octane to reduce its vapour pressure to 80%.
23.There were cases of death due to medical negligence during operations due to the use of ethyl ether as anaesthetic. Today alternate anaesthetic is being used as CF3CHBrCl (haloethane).
Based on the above passage, answer the following questions.
(i)CF3CHBrCl is being used as anaesthetic. What benefits it might have over ether compounds in a normal surgical environment reminding you that, operating rooms usually contain pure oxygen supplies?
(ii)Mark stereocentre (if any) in haloethane
(iii)What value will you keep in mind while using haloethane in place of ethyl ether?
Section E
24.For first order decomposition X—– > Y+Z, rate constant is given by -54000 k =(4.6 xl014s-1)e RT
where the energy of activation is in calories. Calculate
(i)temperature at which X would decompose at the rate of 1% per second.
(ii)temperature where decomposition is 80% complete in 1
Or
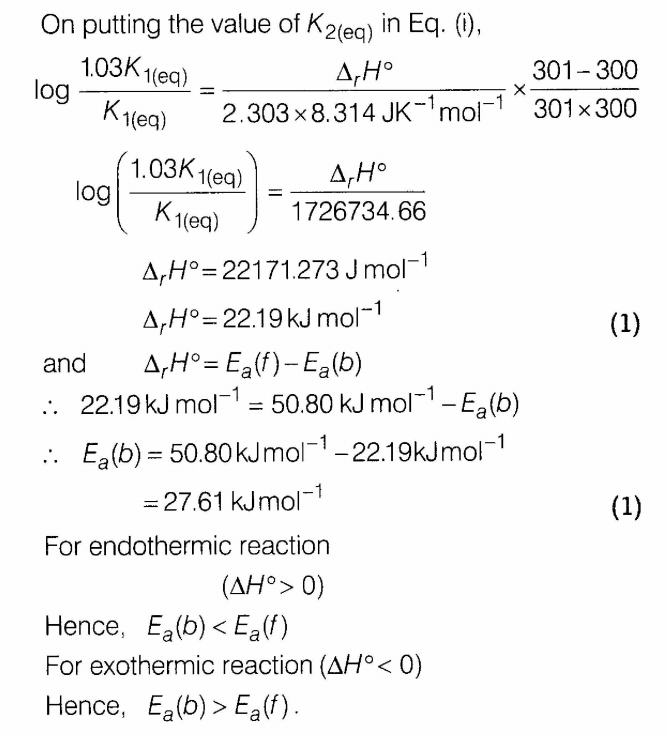
(i) Define activation energy.
(ii)The rate constant of a reaction increases by 7% when its temperature is raised from 300 K to 301 K while its equilibrium constant increases by 3%. Calculate the activation energy of the forward and backward reactions.
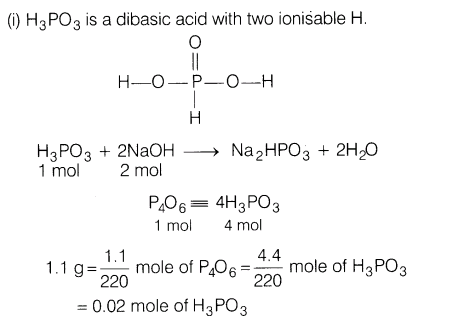
25.(i) P4O6 reacts with H20 according to the equation,P406 + 6H20 ——– > 4H3P03
Calculate the volume of 0.1 M NaOH solution required to neutralise the acid , formed by dissolving 1.1 g of P4Oe in H2o.
(ii) Explain
(a)Bi(V) is a stronger oxidising agent than Sb(V).
(b)The bond angles (O—N—O) have not the same value in NO2 and NO2.
Or
(i)Deduce the shapes of the following on the basis of VSEPR theory.
(a) BrF3 (b) I3 (c) IF7
(ii)Give applications of He, Ne and Ar gases.
26.What is meant by the following terms? Give an example of each.
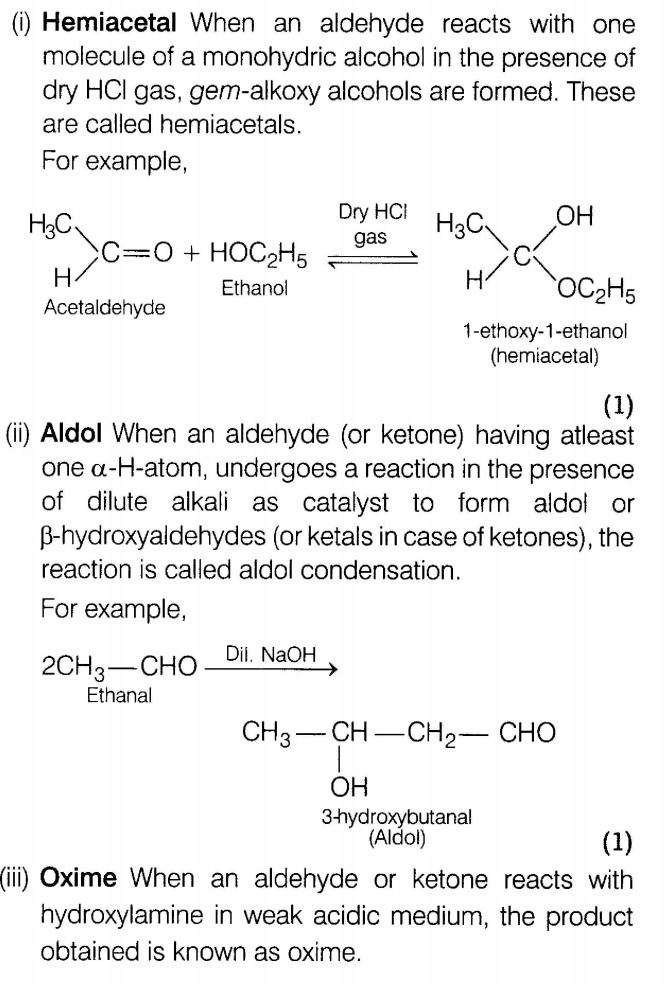
(i)Hemiacetal
(ii)Aldol
(iii)Oxime
(iv)Imine
(v)Schiff’sbase
Or
Complete the following
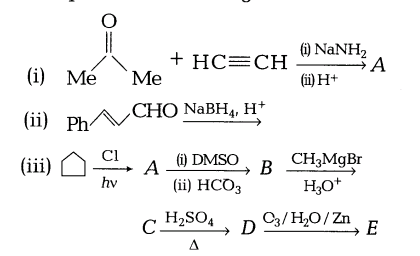
Answers
Section A
1 .State boiling point elevation constant for a solvent
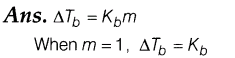
Thus, boiling point elevation constant is equal to the elevation in boiling point when 1 mole of a solute is dissolved in 1 kg of solvent. It is also called ebullioscopic constant.
2.What is denatured alcohol?
Ans. Ethyl alcohol is mixed with some toxic substances such as pyridine, copper sulphate, etc., to make it unfit for drinking purposes. Such alcohol is called denatured alcohol.
3.Explain why alkylamine is more basic than ammonia?
Ans. In alkyl amine (R — NH2), one R—group is present but in ammonia (NH3), all are hydrogen atoms.
Due to the R—group, electron density increases over nitrogen, lone pair of nitrogen becomes more available for donation i.e. its basicity increases.
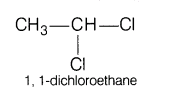
4.Write the IUPAC names of the following:
(i)Ethylidene chloride
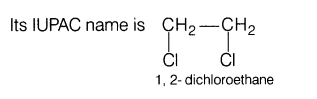
(ii)Ethylene dichloride
Ans. (i) Ethylidene chloride is gem-dichloride in which both Cl-atoms are attached to same carbon atom.
Its IUPAC name is
(ii)Ethylene dichloride is w’c-dihalide in which Cl-atoms are attached to adjacent carbon atoms
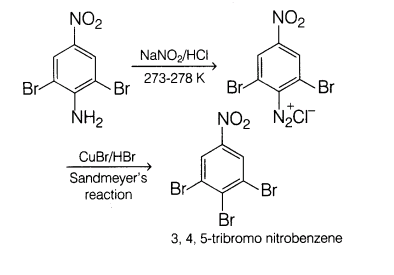
5. How will you bring out the following conversion?

Ans.
Section B
6.An aqueous solution containing 28% by mass of liquid A (molecular mass = 140) has a vapour pressure of 160 mm at 30°C. Find the vapour pressure of the pure liquid A (the vapour pressure of water at 30° C is 150 mm).

7.Define the following terms in relation to crystalline solids.
(i)Unit cell
(ii)Coordination number
Give one example of each case.
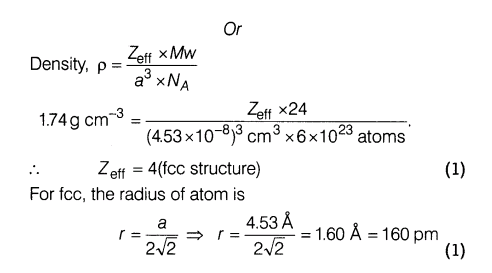
Or
The edge length of unit cell of a metal (molecular weight =24) having cubic structure is 4.53 A. If the density of metal is 1.74 gem-3 , the radius of metal is (Na =6 x 1023 ).
Ans.(i) Unit cell It is the smallest portion of a crystal lattice which when repeated in different directions, generates the entire lattice. For example, primitive unit cells and centred unit cells.

8.Chromium metal crystallises in a body centred cubic lattice. The length of the unit cell edge is found to be 287 pm. Calculate the atomic radius of chromium.

9.The standard oxidation potential of Ni/Ni2+ electrode is 0.236 V If this is combined with a hydrogen electrode in an acidic solution, at what pH of the solution will measured EMF be zero at 25°C? [Assuming [Ni2+ ] = 1M]
Ans.
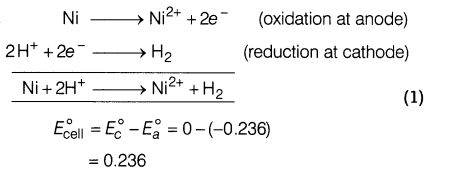
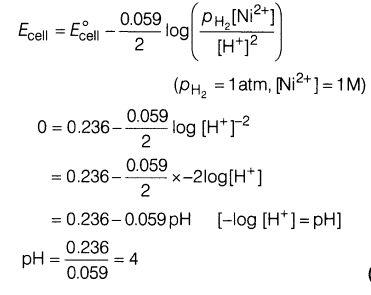
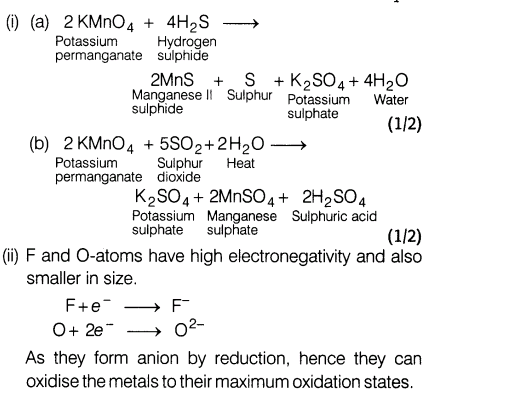
10.(i)(a) Give the reaction when KMnO4 reacts with H2 S in neutral medium.
(b) Reaction of KMn04 with S02 in acidic medium.
(ii) Why the highest oxidation state of a metal exhibited in its oxide or fluoride form only?
Ans.
Section C
11.(i)Out of Cu2Cl2 and CuCl2, which is more stable? Why?
(ii) While filling up of electrons in the atomic orbitals, the 4s-orbital is filled before the 3d-orbital but reverse happens during the ionisation of the atom. Explain.
Ans.


Thus, 4s is filled before 3d.During ionisation, 4s electron is taken out as it is loosely bound to nucleus as compared to 3d electrons.
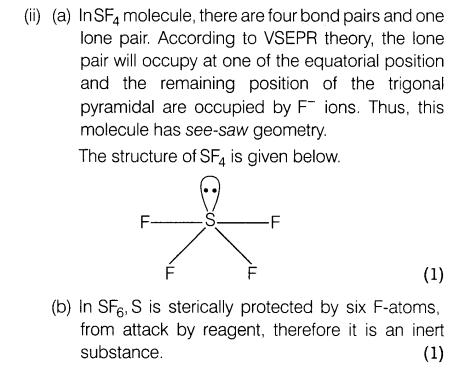
12.(i) NCI3 is an endothermic compound while, NF3 is an exothermic one. Explain.
(ii) (a) Applying VSEPR theory, draw the probable structure of SF4.
(b) Why SF6 is kinetically an inert substance?
Ans. (i) Heat is absorbed when NCI3 is formed from N2 and Cl2. Heat is evolved when NF3 is formed from N2 and F2
13.(i) Define mutarotation and give one example.
(ii) The two strands of DNA are not identical but are complementary? Explain.
Ans. (i) The change in specific rotation of an optically active compound in aqueous solutions is called mutarotation, e.g. in aqueous solution, glucose exist as
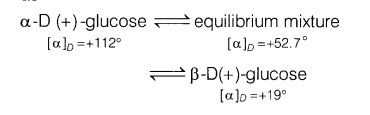
(ii) DNA is a double stranded molecule. The two strands are complementary to each other because H-bonds are formed by specific pairs of bases, i.e. adenine (A) is attached with thymine (T) by two H-bonds and guanine (G) is attached to cytosine (C) by three H-bonds. The other combination of bases are energetically less favoured and hence, do not occur in normal DNA.
14.An aromatic compound A on treatment with aqueous ammonia and heating forms compound B which on heating with Br2 and KOH forms a compound C of molecular formula C6H7 Write the structures and IUPAC names of compounds A, Band C.

Ans.
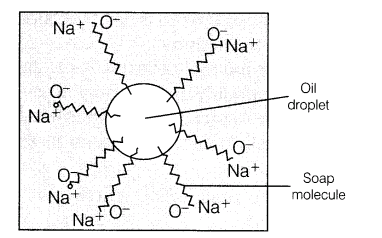
15.Explain the cleansing action of soaps.
Or
(i)How will you define an antacid?
(ii)Name a broad spectrum antibiotic and state two diseases for which it is prescribed.
Ans.
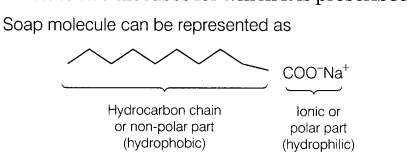
Hydrocarbon chain is water repelling and ionic part is water attracting. When soap is dissolved in water and a dirty cloth is agitated in the solution, the oily dirt attaches to the hydrocarbon part while, water attaches to the ionic part.
Now, these soap molecules arrange themselves in the form of micelles. As the mixture is agitated more, the more and more dirt particles leave the cloth and get attached to the soap molecules. The negative charges of micelles prevent the dirt to form aggregates.Thus, soap removes dirt by reducing the surface tension of water
(i)The substances which neutralise the excess of HCI by preventing the interaction of histamins with the receptor present in the stomach wall are called antacids, e.g. cimetidine and ranitidine.
(ii)Chloramphenicol is a broad spectrum antibiotic. It can be given for treating diseases like pneumonia, dysentry, typhoid, etc.
16.Explain the formation of Helmholtz electrical double layer.
Ans. Colloidal particles always carry an electric charge.
This charge on the sol particle is due to
(i)electron capture by sol particles during electron dispersion of metals.
(ii)preferential adsorption of ions (always a common ion is absorbed) from solution and/or due to the formulation of electrical double layer.

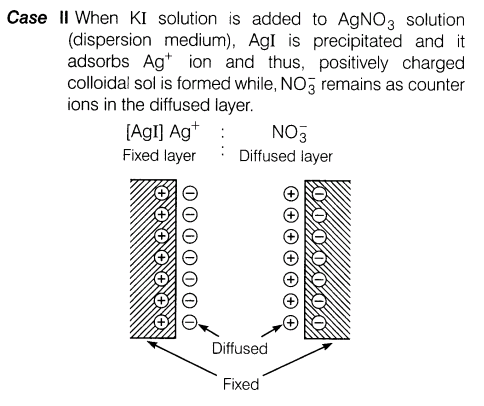
The combination of the two layers of opposite charges around colloidal particle, is called Helmholtz electrical double layer. A potential difference is set up between these two layers and is called electrokinetic potential or zeta potential.
The presence of equal and similar charges on colloidal particles provides stability to colloidal sol as repulsive forces due to same charge, prevent them from coming together (aggregating).
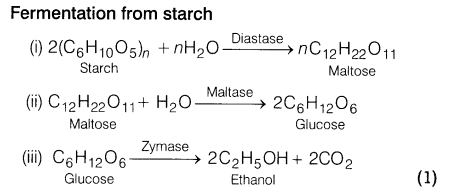
17.Explain a process in which a biocatalyst is used in industrial preparation of a compound.
Ans. Ethanol (ethyl alcohol) can be prepared on industrial scale by fermentation of sugar (present in molasses) or starch (present in rice, barley, etc). In this process, enzymes or biocatalysts present in yeast catalyse the reaction. Fermentation takes place in the absence of air. When carbon dioxide gas is evolved, brisk effervescence is produced.
Following reactions take place during this process :
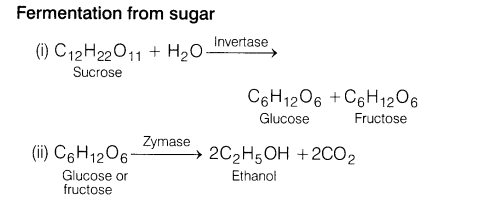
When ethanol formed, exceeds 14% in the solution, the reaction stops. So, fermentation is carried out in dilute solution. The conditions should be anaerobic, because in the presence of air, ethanol oxidises to ethanoic acid
18.(i) Write the IUPAC name of the following molecules.
(a)K3[Co(N03)6]
(b)[Co(NH3)5ONO]2+
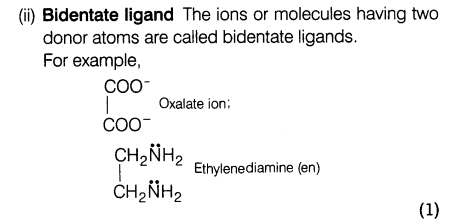
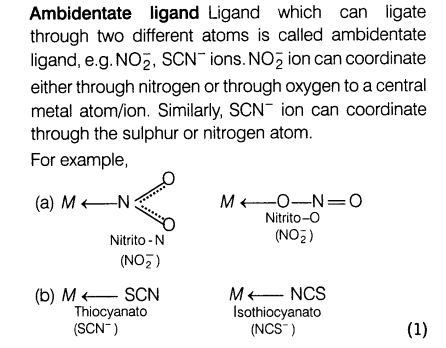
(ii) What is meant by bidentate and ambidentate ligands? Give two examples of each.
Ans.(i) (a) Potassium hexanitratocobaltate (III)
(b) Pentamminenitritocobalt (III) ion
19.Identify A to E and also explain the reactions involved.

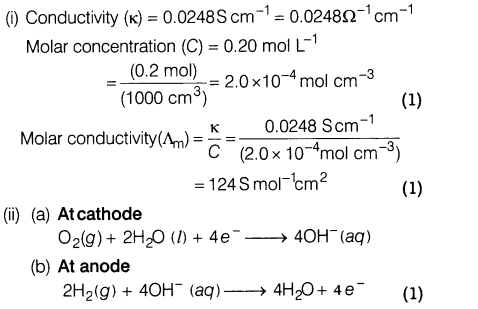
20.(i) The conductivity of 0.20 M solution of KC1 at 298 K is 0.0248 S cm-1 . Calculate its molar conductivity.
(ii) Amongst the fuel cells, H2— 02 fuel cell is most commonly used for providing electrical power in Apollo space programme. The cell runs continuously as long as the reactants are supplied.
Write the reactions occurring at cathode and anode.
Ans.
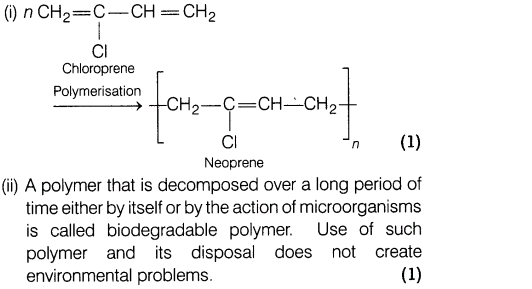
21.(i) Write the preparation of neoprene.
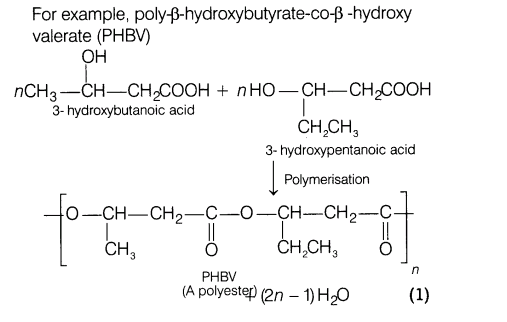
(ii) What is a biodegradable polymer? Give an example of a biodegradable aliphatic polyester (with reaction).
Ans.
22.Calculate the mass of a non-volatile solute (molar mass = 40 g mol-1) which should be dissolved in 114 g octane to reduce its vapour pressure to 80%.
23.There were cases of death due to medical negligence during operations due to the use of ethyl ether as anaesthetic. Today alternate anaesthetic is being used as CF3CHBrCl (haloethane).
Based on the above passage, answer the following questions.
(i)CF3CHBrCl is being used as anaesthetic. What benefits it might have over ether compounds in a normal surgical environment reminding you that, operating rooms usually contain pure oxygen supplies?
(ii)Mark stereocentre (if any) in haloethane
(iii)What value will you keep in mind while using haloethane in place of ethyl ether?
Ans.(i) Ethyl ether (called ether) was an important general anaesthetic, first used in surgery in 1840. It is seldom in use today because it has a tendency to form explosive peroxide in containers left exposed to air and due to use of 02 in surgical operations. This type of reaction is avoided with haloethane
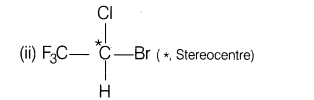
(iii)The value to be kept in mind while using haloethane in place of ethyl ether is concerness
Section E
24.For first order decomposition X—– > Y+Z, rate constant is given by -54000 k =(4.6 xl014s-1)e RT
where the energy of activation is in calories. Calculate
(i)temperature at which X would decompose at the rate of 1% per second.
(ii)temperature where decomposition is 80% complete in 1
Or
(i) Define activation energy.
(ii)The rate constant of a reaction increases by 7% when its temperature is raised from 300 K to 301 K while its equilibrium constant increases by 3%. Calculate the activation energy of the forward and backward reactions.
Ans.
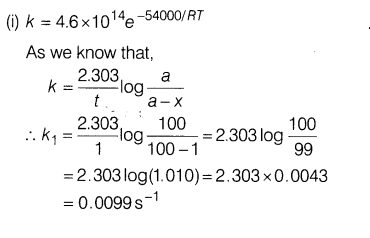
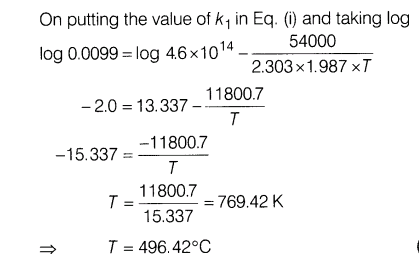
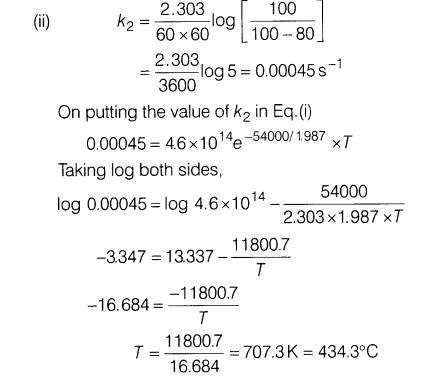

25.(i) P4O6 reacts with H20 according to the equation,P406 + 6H20 ——– > 4H3P03
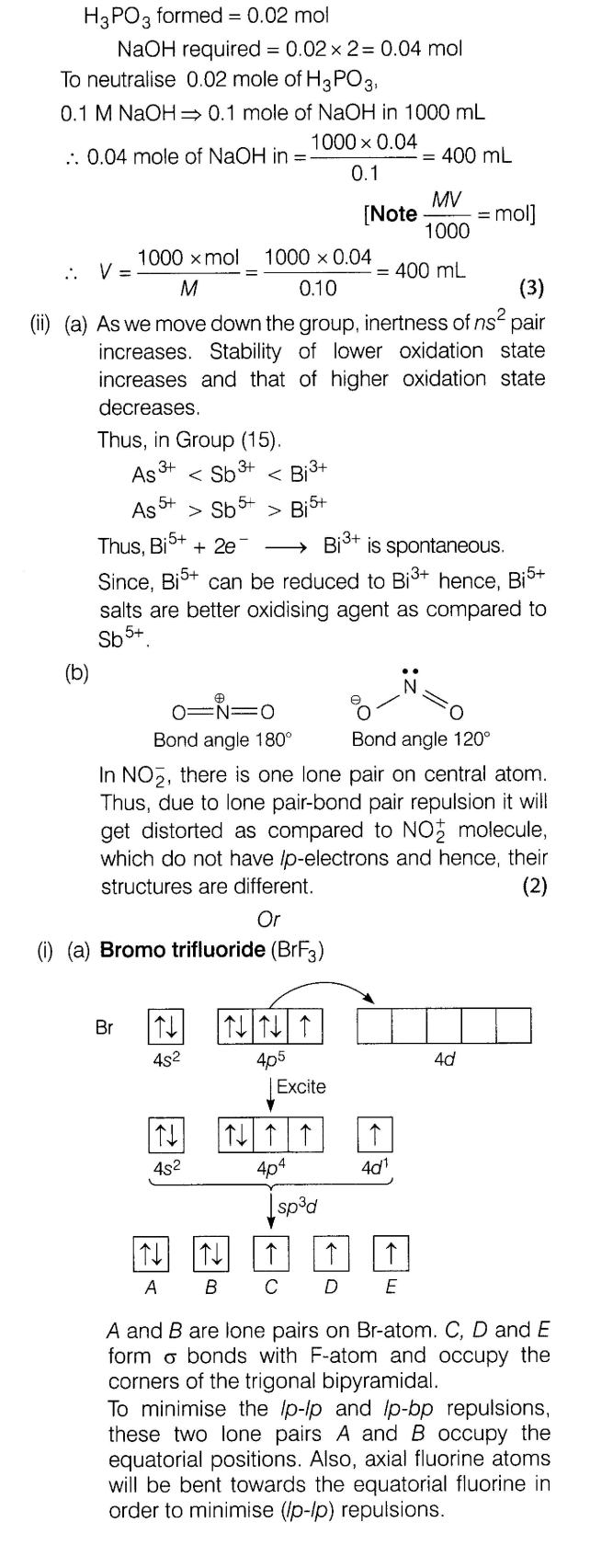
Calculate the volume of 0.1 M NaOH solution required to neutralise the acid , formed by dissolving 1.1 g of P4Oe in H2o.
(ii) Explain
(a)Bi(V) is a stronger oxidising agent than Sb(V).
(b)The bond angles (O—N—O) have not the same value in NO2 and NO2.
Or
(i)Deduce the shapes of the following on the basis of VSEPR theory.
(a) BrF3 (b) I3 (c) IF7
(ii)Give applications of He, Ne and Ar gases.
Ans.
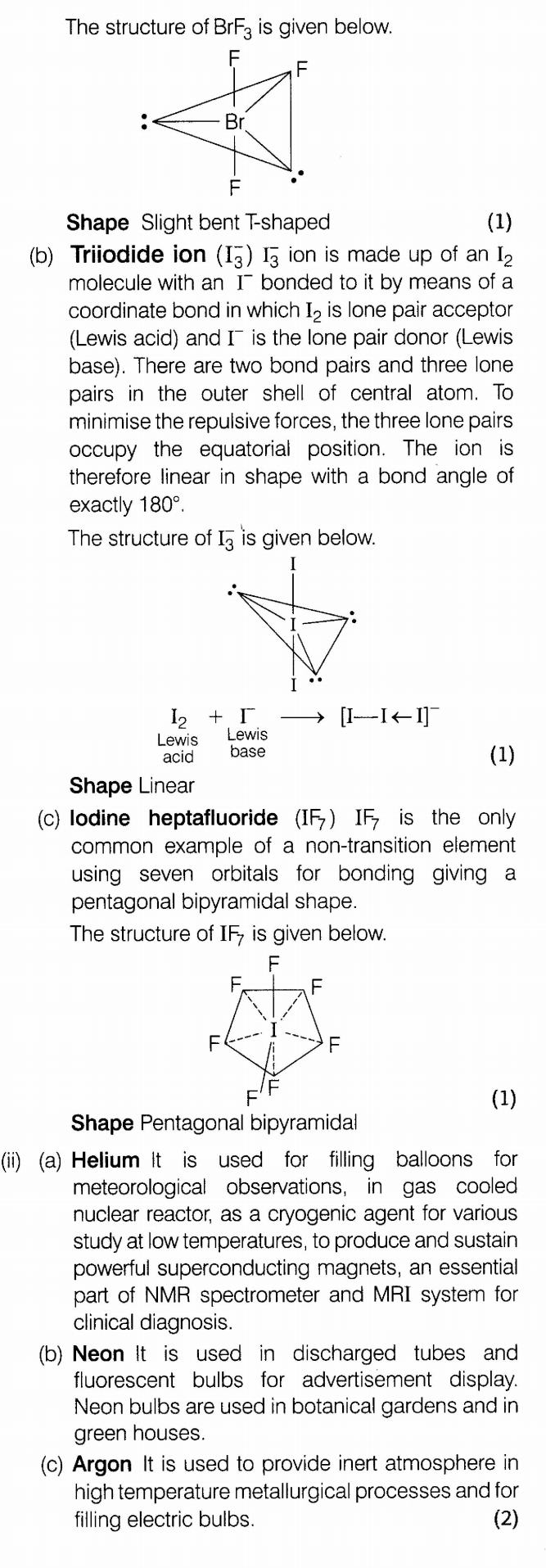
26.What is meant by the following terms? Give an example of each.
(i)Hemiacetal
(ii)Aldol
(iii)Oxime
(iv)Imine
(v)Schiff’sbase
Or
Complete the following

Ans.
(Download Questions PDF)
(Download Solutions PDF)
<!–
–>