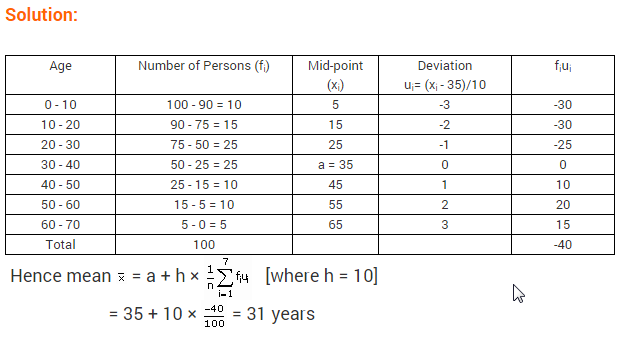
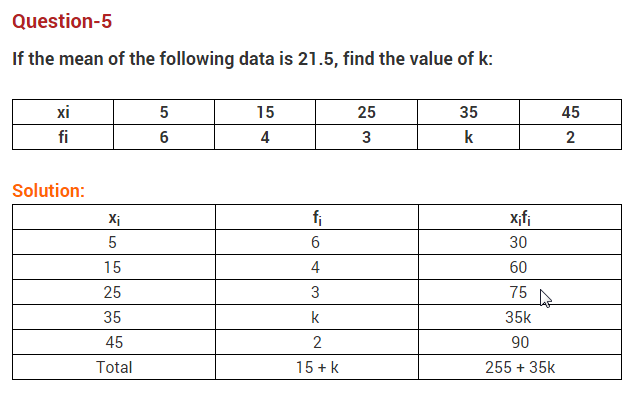
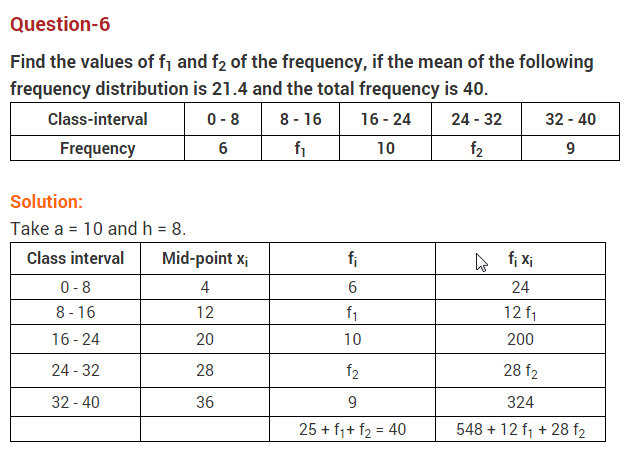
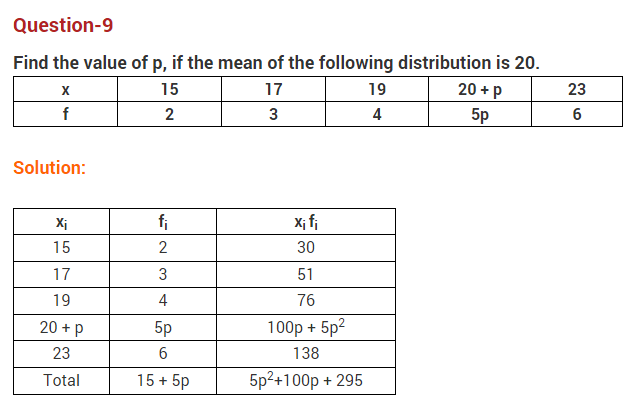
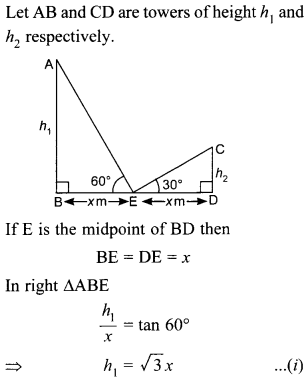
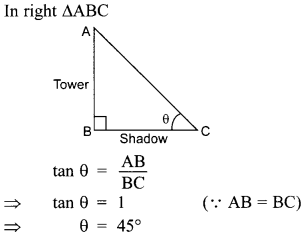
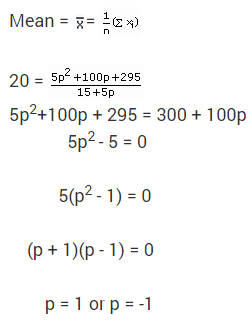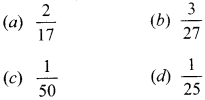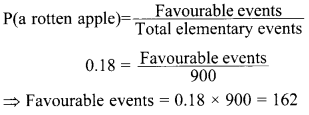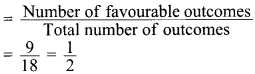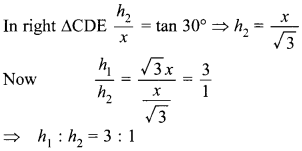Free PDF Download of CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Probability Multiple Choice Questions with Answers. MCQ Questions for Class 10 Maths with Answers was Prepared Based on Latest Exam Pattern. Students can solve NCERT Class 10 Maths Probability MCQs with Answers to know their preparation level.
Class 10 Maths MCQs Chapter 15 Probability
MCQ On Probability Class 10 Question 1. The probability of getting exactly one head in tossing a pair of coins is
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 1/3
(d)1/2
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination: Reason: S = [HH, HT, TH, TT] = 4
∴ P(exactly 1 head) =24=12
MCQ Questions For Class 10 Maths Probability Question 2. The probability of getting a spade card from a well shuffled deck of 52 cards is

Answer/ Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination: Reason: Total cards = 52,
Spade cards = 13
∴ P(a spade card) =1352=14
Probability MCQ Class 10 Question 3. The probability of getting less than 3 in a single throw of a die is

Answer/ Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination: Reason: Here S = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
∴ n(S) = 6
E = (Less than 3) = [1, 2
∴ P(Less than 3) =26=13
Probability Class 10 MCQ Question 4. The total number of events of throwing 10 coins simultaneously is
(a) 1024
(b) 512
(c) 100
(d) 10
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination: Reason: Total events 210 = 1024
MCQ Of Probability For Class 10 Question 5. Which of the following can be the probability of an event?
(a) – 0.4
(b) 1.004
(c) 1823
(d) 107
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination: Reason: The probability of an event can neither be a negative value, nor it can exceed unity.
Probability MCQs With Answers Pdf Question 6. Three coins are tossed simultaneously. The probability of getting all heads is

Answer/ Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination: Reason: Here S = [HHH, HHT, HTH, THH, HTT, THT, TTH, TTT] = 8
∴ P(all heads) = 18
Probability MCQ Question 7. One card is drawn from a well shuffled deck of 52 cards. The probability of getting a king of red colour is
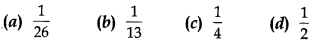
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination: Reason: Total cards = 52
Total events «(S) = 52
a king of red colour = 2
P(a king of red colour) =252=126
MCQ Questions For Class 10 Maths With Answers Question 8. One card is drawn from a well shuffled deck of 52 playing cards. The probability of getting a non-face card is
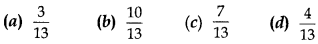
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination: Reason; Total cards = 52,
Total face cards = 12
∴ Non-face cards = 52 – 12 = 40
∴ P(a non-face card) =4052=1013
9. The chance of throwing 5 with an ordinary die is

Answer/ Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination: Reason: Here S = [1, 2, 3,4, 5, 6]
∴ n(S) = 6
∴ P(throwings) = 16
MCQ Questions For Class 10 Maths Question 10. The letters of the word SOCIETY are placed at random in a row. The probability of getting a vowel is

Answer/ Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination: Reason: Totle letters = 7
No. of vowel = 3 [∵ Vowel are O, I, E]
∴ P(a vowel) = 37
Probability Questions And Answers Pdf Question 11. Cards bearing numbers 3 to 20 are placed in a bag and mixed thoroughly. A card is taken out from the bag at random. The probability that the number on the card taken out is an even number, is

Answer/ Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination: Reason: Total cards = 18
Cards with even numbers are 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20 = 9
∴ P(even number) =918=12
Maths MCQ For Class 10 Question 12. The total events to throw three dice simultaneously is
(a) 6
(b) 18
(c) 81
(d) 216
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination: Reason: Total cards = (6)3= 216
10 Class Maths MCQ With Answers Question 13. The probability of getting a consonant from the word MAHIR is

Answer/ Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination: Reason: Total characters in MAHIR = 5,
Consonants are M, H, R i.e., 3
∴ P(getting a consonant) = 35
Probability Multiple Choice Questions Question 14. A girl calculates that the probability of her winning the first prize in a lottery is 8100. If 6,000 tickets are sold, how many tickets has she bought?
(a) 400
(b) 750
(c) 480
(d) 240
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination: Reason: No. of tickets sold = 8100 × 6000 = 8 ×60 = 480
Multiple Choice Questions On Probability Question 15. A card is drawn from a well shuffled deck of 52 cards. The probability of a seven of spade is
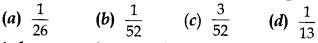
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination: Reason: Total cards = 52, A seven of spade = 1
∴ P(a seven of spade) = 152
Probability Multiple Choice Questions And Answers Question 16. A bag contains 3 red balls and 5 black balls. A ball is drawn at random from the bag. The probability that a red ball drawn is
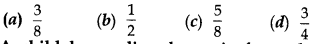
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination: Reason: Total balls = 3 + 5 = 8
∴ Total events = 8
P(a red ball) = 38
Probability MCQ Pdf Question 17. A child has a die whose six faces show the letters as given below:
The die is thrown once. The probability of getting a ‘D’ is
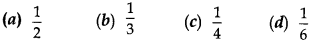
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination: Reason: Sample space S = [A, B, C, D, E, F] = 6
∴ n(S) = 6
∴ P(getting D) = 16
Probability Multiple Choice Questions And Answers Pdf Question 18. One card is drawn from a well-shuffled deck of 52 cards. The probability that the card will not be an ace is

Answer/ Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination: Reason: Total cards = 52
∴ Total events = 52
No. of ace cards = 4
Non-ace cards = 52 – 4 = 48
∴ P(not an ace) =4852=1213
Probability Multiple Choice Questions Pdf Question 19. A lot consists of 144 ball pens of which 20 ae defective and the others are good. Tanu will buy a pen if it is good but will not buy if it is defective. The shopkeeper draws one pen at random and gives it to her. The probability that she will buy that pen is
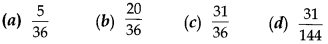
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination: Reason: Total ball pens = 144
Defective ball pens = 20
Good ball pens = 144 – 20 = 124
∴ P(she will buy a pen) = P(good ball pen) =124144=3136
Multiple Choice Probability Questions Question 20. A ticket is drawn at random from a bag containing tickets numbered from 1 to 40. The probability that the selected ticket has a number which is a multiple of 5 is

Answer/ Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination: Reason: Total number = 40
∴ n(S) = 40
Number of favourable events are 5,10,15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40 = 8
∴ Probability (multiple of 5) =840=15
Probability Questions Multiple Choice Question 21. Which of the following cannot be the probability of an event? [Delhi 2011]
(a) 1.5
(b) 35
(c) 25%
(d) 0.3
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination:
(a) ∵ Probability of any event cannot be more than 1.
∴ 1.5 can not be the probability of any event.
∴ (a) is the answer.
Basic Probability Multiple Choice Questions Pdf Question 22. A coin is tossed twice. The probability of getting both heads is [Foreign 2013]

Answer/ Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:
(c) Sample space = {HH, HT, TH, TT}
Number of total possible outcomes =4
Number of favourable outcome (both heads) = 1
∴ Probability of getting both heads = 14
Probability MCQs With Answers Question 23. A fair dice is rolled. Probability of getting a number x such that 1 ≤ x ≤ 6, is
(a) 0
(b) > 1
(c) between 0 and 1
(d) 1
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination: (d) 1, ∵ It is a sure event.
24. The sum of the probabilities of all elementary events of an experiment is p, then
(a) 0 < p < 1
(b) 0 ≤ p < 1
(c) p = 1
(d) p = 0
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination: (c) p = 1
25. If an event cannot occur, then its probability is [NCERT Exemplar Problems]
(a) 1
(b) 34
(c) 12
(d) 0
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination: (d) 0. ∵ event cannot occur.
26. An event is very unlikely to happen. Its probability is closest to [NCERT Exemplar Problems]
(a) 0.0001
(b) 0.001
(c) 0.01
(d) 0.1
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination: (a) 0.0001
27. Match the columns:

(a) (1) → (A), (2) → (B), (3) → (C)
(b) (1) → (B), (2) → (A), (3) → (C)
(c) (1) → (C), (2) → (B), (3) → (E)
(d) (1) → (C), (2) → (B), (3) → (D)
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination: (d) Probability facts
28. A card is drawn from a well-shuffled deck of 52 playing cards. The probability that the card will not be an ace is

Answer/ Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:
(c) Total number of cards = 52
Number of ace = 4
P(not be an ace) = 4852=1213
29. An experiment whose outcomes has to be among a set of events that are completely known but whose exact outcomes is unknown is a
(a) sample space
(b) elementary event
(c) random experiment
(d) none of these
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination: (c) Random experiment
30. The experiments which when repeated under identical conditions produce the same results or outcomes are known as
(a) random experiments
(b) probabilistic experiment
(c) elementary experiment
(d) deterministic experiment
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination: (d) Deterministic experiment
31. For an event E, P(E) + P(E→) = q, then
(a) 0 ≤ q < 1
(b) 0 < q ≤ 1
(c) 0 < q < 1
(d) none of these
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination:
(d) ∵ P(E) + P(E→) = 1
∴ q = 1
32. A man is known to speak truth 3 out of 4 times. He throws a die and a number other than six comes up. Find the probability that he reports it is a six.

Answer/ Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination:
(b) When a number other than six appears
and man reports it is a six, it means man is telling a lie.
∴ Probability = 1 – 14=14
33. One ticket is selected at random from 100 tickets numbered 0.0, 01, 02, ……, 99. Suppose x is the sum of digits and y is the product of digits, then probability that x = 9 and y = 0 is
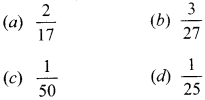
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:
(c) Sum of digits = 9 and product = 0
∴ Number is either 09 or 90.
∴ Required probability = 2100=150
34. A bag contains 5 black balls, 4 white balls and 3 red balls. If a ball is selected randomwise, the probability that it is a black or red ball is ____ .
Answer/ Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Number of black or red balls = 5 + 3
= 8
∴ Required probability = 812=23
35. The probability of a non-leap year having 53 Mondays is _______. [Foreign 2012]
Answer/ Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
No. of days in a non-leap year = 365
No. of complete weeks = 52(52 × 7 = 364)
No. of days left = 1
∴ Probability of this day being a Monday = Probability of 53 Mondays = 17
36. If a random experiment is performed, then each of its outcomes is known as ______ .
Answer/ Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: elementary event
37. The probability of selecting a rotten apple randomly from a heap of 900 apples is 0.18. What is the number of rotten apples in the heap? [AI2017]
Answer/ Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Total apples in the heap = 900
∴ Total number of elementary events = 900
One rotten apple is randomly selected from this heap
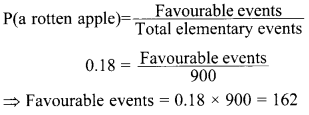
Hence, there are 162 rotten apples in the heap.
38. From a well shuffled pack of cards, a card is drawn at random. Find the probability of getting a black queen.
Answer/ Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Total number of ways to draw a card = 52
Number of ways to draw a black queen = 2
∴ Probability of getting a black queen 252=126
39. If three different coins are tossed together, then find the probability of getting two heads. [AI 2017 (C)]
Answer/ Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Three coins are tossed together.
Possible outcomes
{HHH, HHT, HTH, THH, TTT, TTH, THT, HTT}
Number of 2 heads together = 3 Probability of getting two heads = 38
40. A die is thrown once. Find the probability of getting a number less than 3.
Answer/ Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Total number of ways = 6
Number of ways to get a number less than 3 = 2
∴ Required probability = 26=13
41. Cards bearing numbers 3 to 20 are placed in a bag and mixed thoroughly. A card is taken out from the bag at random. What is the probability that the number on the card taken out is an even number?
Answer/ Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Total number of cards =18
Even numbers from 3 to 20 are 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20 = 9 numbers
Probability that the number on the card taken out is an even number
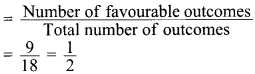
42. Two coins are tossed simultaneously. Find the probability of getting exactly one head.
Answer/ Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
When two coins are tossed simultaneously
Total number of outcomes = {HH, HT, TH, TT}
Total number of outcomes = 4
Favourable outcomes = {HT, TH} = 2
Probability of getting exactly one head = 24=12
43. An unbiased die is thrown, what is the probability of getting an even number.
Answer/ Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Total outcomes = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
Favourable outcomes = {2, 4, 6}
∴ Probability of getting an even number = 36=12
44. If the probability of winning a game is 0.3, what is the probability of losing it?
Answer/ Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Probability of winning a game = 0.3
∴ Probability of losing the game
= 1 – Probability of winning the game
= 1 – 0.3 = 0.7
45. A man is known to speak truth 5 out of 7 times. He throws a die and a number other than 6 comes up. Find the probability that he reports it is a six.
Answer/ Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
P(man will speak the truth) = 57
∴ P(man will not speak the truth) = 1 – 57=27
when a number other than 6 comes up the probability of man’s reporting it is a six the probability of man not speaking the truth 57
We hope the given MCQ Questions for Class 10 Maths Probability with Answers will help you. If you have any query regarding CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Probability Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.