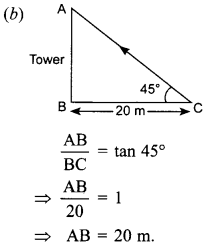
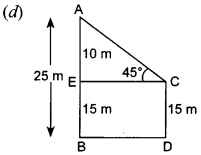
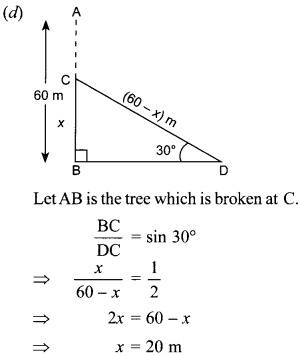
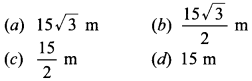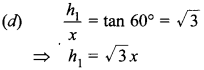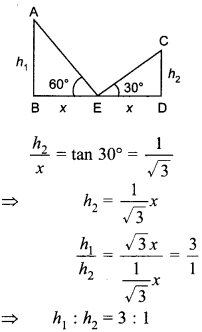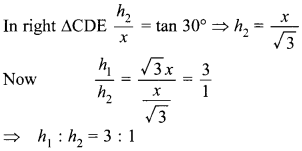Free PDF Download of CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circles Multiple Choice Questions with Answers. MCQ Questions for Class 10 Maths with Answers was Prepared Based on Latest Exam Pattern. Students can solve NCERT Class 10 Maths Circles MCQs with Answers to know their preparation level.
Class 10 Maths MCQs Chapter 10 Circles
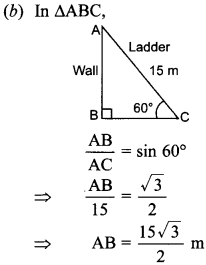
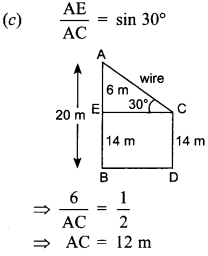
Circle Multiple Choice Question 1. The distance between two parallel tangents of acircle of radius 4 cm is
(a) 2 cm
(b) 4 cm
(c) 6 cm
(d) 8 cm
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination:
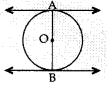
Reason: Here radius, r = 4 cm
Required distance,
AB = OA + OB
= r + r = 2r = 2×4 = 8 cm
2. In the given figure, if ZRPS = 25°, the value of ZROS is
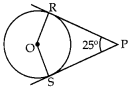
(a) 135°
(b) 145°
(c) 165°
(d) 155°
Answer/ Explanation
Circles Class 10 MCQ With Answer: dExplaination: Reason: Since OR ⊥ PR and OS ⊥ PS
∴ ∠ORP = ∠OSP = 90°
In □ ORPS, ∠ROS + ∠ORP + ∠RPS + ∠OSP = 360°
∠ROS + 90° + 25° + 90° = 360°
∠ROS = 360° – 205° = 155°
3. A tangent is drawn from a point at a distance of 17 cm of circle C(0, r) of radius 8 cm. The length of its tangent is
(a) 5 cm
(b) 9 cm
(c) 15 cm
(d) 23 cm
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:
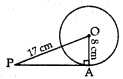
Reason: In rt ∆OAP, AP² + OA² = OP²
⇒ AP² + (8)² = (17)² => AP² + 64 = 289
⇒ AP² = 289 – 64 = 225
∴ AP = √225 = 15 cm
4. The length of tangents drawn from an external point to the circle
(a) are equal
(b) are not equal
(c) sometimes are equal
(d) are not defined
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination: Reason: Since the length of tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are equal.
5. Number of tangents drawn at a point of the , circle is/are
(a) one
(b) two
(c) none
(d) infinite
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination: Reason: There is only one tangent at a point of the circle.
6. The tangents drawn at the extremities of the diameter of a circle are
(a) perpendicular
(b) parallel
(c) equal
(d) none of these
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination:
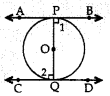
Reason: Since OP ⊥ AB and OQ ⊥ CD
∴ Z1 = 90° and Z2 = 90°
⇒ ∠1 = Z2, which are alternate angles.
∴ AB || CD
7. Tangents from an external point to a circle are
(a) equal
(b) not equal
(c) parallel
(d) perpendicular
Answer/ Explanation
MCQs of Maths for Class 10 With Answer: aExplaination: Reason: Tangents from external points to a circle are equal.
8. The length of a tangent drawn from a point at a distance of 10 cm of circle is 8 cm. The radius of the circle is
(a) 4 cm
(b) 5 cm
(c) 6 cm
(d) 7 cm
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:
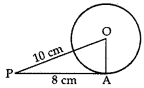
Reason: In rt. AOAP, we have
OA² + AP² = OP²
⇒ OA² + (8)² = (10)2
⇒ OA² + 64 = 100
⇒ OA² = 100 – 64 = 36
∴ OA = √36 = 6 cm
MCQ Questions on Circles for Class 10 Question 9. In given figure, CP and CQ are tangents to a circle with centre O. ARB is another tangent touching the circle at R. If CP = 11 cm and BC = 6 cm then the length of BR is
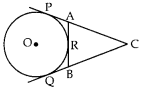
(a) 6 cm
(b) 5 cm
(c) 4 cm
(d) 3 cm
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination: Reason: Since
BQ = BR …(i) [∵ Tangents drawn from external points are equal]
CQ = CP …[Using (i)]
BC + BQ = 11
⇒ 6 + BR = 11
⇒ BR = 11 – 6 = 5 cm
10. From a point P which is at a distance of 13 cm from the centre O of a circle of radius 5 cm, the pair of tangents PQ and PR to the circle are drawn. Then the area of the quadrilateral PQOR is
(a) 60 cm²
(b) 65 cm²
(c) 30 cm²
(d) 32.5 cm²
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination:
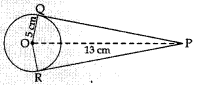
Reason: OP² = OQ² + PQ²
169 = 25 + PQ²
PQ² = 144
PQ = 12
Area PQOR = ar (AOPQ) + ar (AOPR)
= 12 × 12 × 5 + 12 × 12 × 5 = 60 cm²
MCQ Questions for Class 10 Maths Question 11. In the given figure, AB and AC are tangents to the circle with centre O such that ∠BAC = 40°, then ∠BOC is equal to [AI2011]
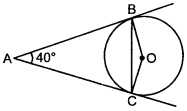
(a) 40°
(b) 50°
(c) 140°
(d) 150°
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:
(c) In quadrilateral ABOC
∠ABO + ∠BOC + ∠OCA + ∠BAC = 360°
⇒ 90° + ∠BOC + 90° + 40° = 360°
⇒ ∠BOC = 360° – 220° = 140°
12. In the given figure, point P is 26 cm away from the centre O of a circle and the length PT of the tangent drawn from P to the circle is 24 cm. Then the radius of the circle is [Foreign 2011]
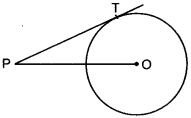
(a) 25 cm
(b) 26 cm
(c) 24 cm
(d) 10 cm
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination: (d) v OT is radius and PT is tangent
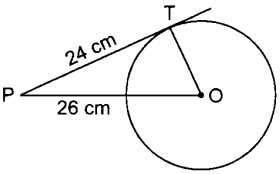
∴ OT ⊥ PT
Now, in AOTP,
⇒ OP² = PT² + OT²
⇒ 26² = 24² + OT²
⇒ 676 – 576 = OT²
⇒ 100 = OT²
⇒ 10 cm = OT
13. A line through point of contact and passing through centre of circle is known as
(a) tangent
(b) chord
(c) normal
(d) segment
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination: (c) normal
Maths MCQ for Class 10 Cbse With Answers Pdf Question 14. C (O, r1) and C(O, r2) are two concentric circles with r1 > r2 AB is a chord of C(O, r1) touching C(O, r,2) at C then
(a) AB = r1
(b) AB = r2
(c) AC = BC
(d) AB = r1 + r2
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:
(c) ∵ AB touches
C(0, r<sub>2</sub>)
∴ OC ⊥ AB
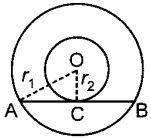
Also, perpendicular from the centre to a chord bisects the chord.
∴ AC = BC
15. Two parallel lines touch the circle at
points A and B respectively. If area of the circle is 25 n cm2, then AB is equal to
(a) 5 cm
(b) 8 cm
(c) 10 cm
(d) 25 cm
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:
(c) Let radius of circle = R
∴ πR² = 25π
⇒ R = 5 cm
∴ Distance between two parallel tangents = diameter = 2 × 5 = 10 cm.
MCQ Questions for Class 10 Maths Circles Question 16. From a point P which is at a distance of 13 cm from the centre O of a circle of radius 5 cm, the pair of tangents PQ and PR to the circle are drawn. Then the area of the quadrilateral PQOR is [NCERT Exemplar Problems]
(a) 60 cm²
(b) 65 cm²
(c) 30 cm²
(d) 32.5 cm²
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination:
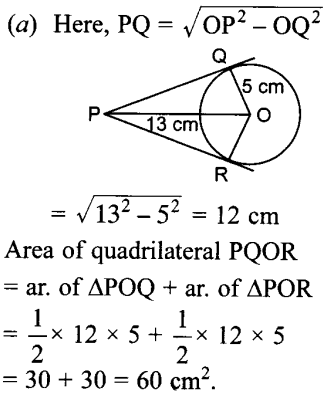
17. In figure AT is a tangent to the circle with centre O such that OT = 4 cm and ∠OTA = 30°. Then AT is equal to [NCERT Exemplar Problems]
(a) 4 cm
(b) 2 cm
(c) 2√3 cm
(d) 4√3 cm
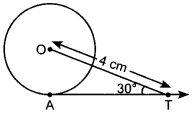
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:
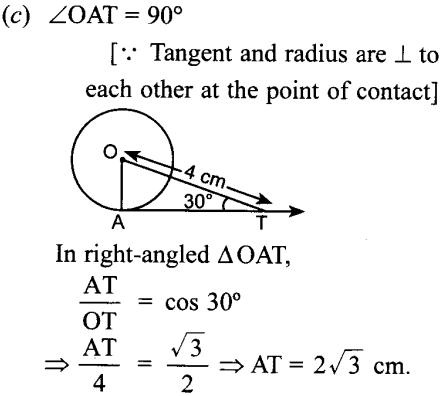
18. In figure if O is centre of a circle, PQ is a chord and the tangent PR at P makes an angle of 50° with PQ, then ∠POQ is equal to [NCERT Exemplar Problems]
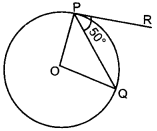
(a) 100°
(b) 80°
(c) 90°
(d) 75°
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination:
(a) OP ⊥ PR [Y Tangent and radius are ⊥ to each other at the point of contact]
∠OPQ = 90° – 50° = 40°
OP = OQ [Radii]
∴ ∠OPQ = ∠OQP = 40°
In ∆OPQ,
⇒ ∠POQ + ∠OPQ + ∠OQP = 180°
⇒ ∠POQ + 40° + 40° = 180°
∠POQ = 180° – 80° = 100°.
19. Match the column:
| (1) The tangent at any point of a circle is … | (A) known as tangent to the circle |
| (2) The line containing the radius through the point of contact is … | (B) to the radius through the point of |
| (3) The lengths of tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are… | (C) called the ‘normal’ to circle |
| (4) When two end points of the corresponding chord of a secant coincide, it is … | (D) equal |
(a) 1 → A, 2 → B, 3 → C, 4 → D
(b) 1 → B, 2 → A, 3 → D, 4 → C
(c) 1 → D, 2 → A, 3 → C, 4 → B
(d) 1 → B, 2 → C, 3 → D, 4 → A
Answer/ Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Properties of circle.
Questions on Circles for Class 10 Question 20. In figure, O is the centre of a circle, AB is a chord and AT is the tangent at A. If ∠AOB = 100°, then ∠BAT is equal to [Delhi 2011]
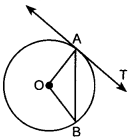
(a) 100°
(b) 40°
(c) 50°
(d) 90°
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:
(c) ∠AOB = 100°
∠OAB = ∠OBA (∵ OA and OB are radii)
Now, in ∆AOB,
∠AOB + ∠OAB + ∠OBA = 180°
(Angle sum property of A)
⇒ 100° + x + x = 180° [Let ∠OAB = ∠OBA = x]
⇒ 2x = 180° – 100°
⇒ 2x = 80°
⇒ x = 40°
Also, ∠OAB + ∠BAT = 90°
[∵ OA is radius and TA is tangent at A]
⇒ 40° + ZBAT = 90°
⇒ ∠BAT = 50°
21. In the figure PA and PB are tangents to the circle with centre O. If ∠APB = 60°, then ∠OAB is [Delhi 2011]
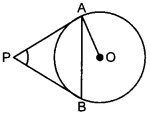
(a) 30°
(b) 60°
(c) 90°
(d) 15°
Answer/ Explanation
MCQ Questions for Class 10 Maths With Answer: a
Explaination:
(a) Given ∠APB = 60°
∵ ∠APB + ∠PAB + ∠PBA = 180°
⇒ APB + x + x = 180°
[∵ PA = PB ∴ ∠PAB = ∠PBA = x (say)]
⇒ 60° + 2x = 180°
⇒ 2x = 180° – 60°
⇒ 2x = 120°
⇒ x = 120°2 = 60°
Also, ∠OAP = 90°
⇒ ∠OAB + ∠PAB = 90°
⇒ ∠OAB + 60°= 90°
⇒ ∠OAB = 30°
Maths Multiple Choice Questions With Answers for Class 10 Question 22. In the given figure, TP and TQ are two tangents to a circle with centre O, such that ∠POQ = 110°. Then ∠PTQ is equal to [Foreign 2011]
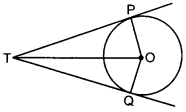
(a) 55°
(b) 70°
(c) 110°
(d) 90°
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination:
(b) In quadrilateral POQT,
∠PTQ + ∠TPO + ∠TQO + ∠POQ
= 360°
⇒ ∠PTQ + 90° + 90° + 110° = 360°
⇒ ∠PTQ + 290° = 360°
⇒ ∠PTQ = 360° – 290° = 70°
23. Infigure,PQandPRaretangentstoacirclewith centreA. If ∠QPA=27°, then ∠QAR equals to [Foreign 2012]
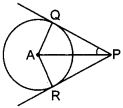
(a) 63°
(b) 153°
(c) 110°
(d) 90°
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:
(c) ∠QPA = ∠RPA
[∵ ∆AQP ≅ ∆ARP (RHS congruence rule)]
⇒ ∠RPA = 27°
∴ ∠QPR = ∠QPA + ∠RPA
= 27° + 27° = 54°
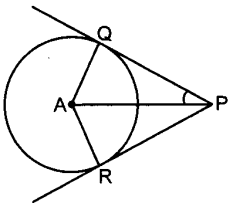
Now,
∠QAR + ∠AQP + ∠ARP + ∠QPR = 360°
⇒ ∠QAR = 90° + 90° + 54° = 360°
⇒ ∠QAR = 360° – 234° = 126°
Circles MCQ Class 10 Question 24. In figure if PQR is the tangent to a circle at Q whose centre is O, AB is a chord parallel to PR and ∠BQR = 70°, then ∠AQB is equal to [NCERT Exemplar Problems]
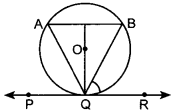
(a) 20°
(b) 40°
(c) 35°
(d) 45°
Answer/ Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
(b) AB || PR
∴ ∠ABQ =∠BQR
[Alternate interior angles]
⇒ ∠ABQ = 70°
Also, ∠BQR = ∠BAQ [Angles in alternate segment]
⇒ ∠BAQ = 70°
In ∆AQB,
∠BAQ + ∠ABQ + ∠AQB = 180°
⇒ 70° + 70° + ∠AQB = 180°
⇒ ∠AQB = 180° – 140° = 40°.
25. The common point of the tangent and the circle is called _____ .
Answer/ Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: point of contact
26. Two concentric circles are of radii 13 cm and 5 cm. The length of the chord of larger circle which touches the smaller circle is _____ .
Answer/ Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: 24 cm. Hint: ∵ AB touches the smaller circle
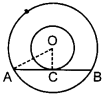
∴ OC ⊥ AB and hence AC = BC
In right ∆OCA,
OA² = OC² + AC²
⇒ AC²= 13² – 5²
⇒ AC = 12
∴ AB = 2 × 12 = 24 cm.
MCQ on Circles Class 10 Question 27. A quadrilateral ABCD is drawn to circumscribe a circle. If AB =12 cm, BC = 15 cm and CD = 14 cm, then AD is equal to _____ .
Answer/ Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: 11 cm. Hint: AB + CD = BC + AD
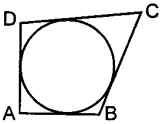
⇒ 12+ 14= 15+ AD
⇒ AD =11 cm.
28. Number of tangents to a circle which are parallel to a secant is ____ .
Answer/ Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: 2
Circle Objective Question 29. A tangent PQ at a point P of a circle of radius 7 cm meets a line through centre O at a point Q so that OQ = 25 cm length PQ is ____ .
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: 24 cm
Explaination:
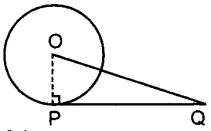
24 cm.
Hint: PQ² = OQ² – OP² = 252²- 7²
⇒ PQ = 24 cm.
30. If the angle between two tangents drawn from an external point P to a circle of radius a and centre O, is 60°, then find the length of OP. [Delhi 2017]
Answer/ Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
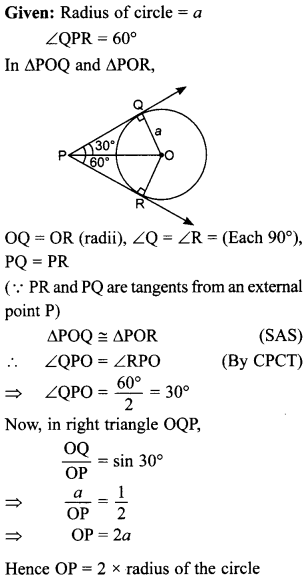
31. In the given fig., there are two concentric circles with centre O. PRT and PQS are tangents to the inner circle from a point P lying on the outer circle. If PR = 5 cm, find the length of PS. [Delhi 2017 (C)]
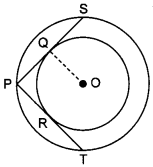
Answer/ Explanation
Circle MCQ With Answer:
Explanation:
PR and PQ are tangents to the circle from common external point P.
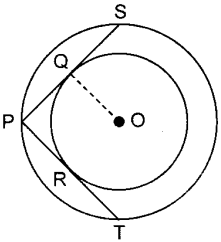
∴ PR = PQ
∴ PQ = 5 cm (∵ PR = 5 cm)
PS = 2PQ (∵ OQ ⊥ PS)
= 2 × 5 = 10 cm
Circle MCQ Pdf Question 32. In the given Fig., O is the centre of the circle, PQ is a chord and PT is tangent to the circle at P. If ∠POQ = 70°, find ∠TPQ. [AI 2017 (C)]
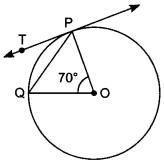
Answer/ Explanation
MCQ on Circles With Answer:
Explanation:
Given: O is centre of the circle, PQ is chord and PT is tangent at P.
To find: ∠TPQ
Solution: In ∆OPQ
∠POQ + ∠OPQ + ∠OQP = 180°
⇒ 70° + ∠OPQ + ∠OPQ = 180°
(∵ OP = OQ, radii of the circle)
⇒ 70° + 2∠OPQ = 180°
⇒ 2∠OPQ = 110°
⇒ ∠OPQ = 55°
OP is perpendicular to the tangent at P.
∴ ∠OPT = 90°
⇒ ∠OPQ + ∠TPQ = 90°
⇒ 55° + ∠TPQ = 90°
⇒ ∠TPQ = 90° – 55°
∠TPQ = 35°
33. What is the distance between two parallel tangents of a circle of radius 7 cm?
Answer/ Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Two parallel tangents of a circle can be drawn only at the end points of the diameter
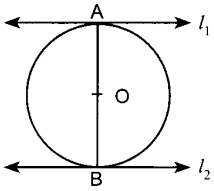
⇒ l<sub>1</sub> || l<sub>2</sub>
⇒ Distance between l<sub>1</sub> and l<sub>2</sub> = AB
= Diameter of the circle
= 2 × r = 2 × 7 cm = 14 cm
MCQ on Circle Question 34. In the given figure, find ∠QSR.
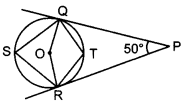
Answer/ Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Given: PQ and PR are tangents to a circle with centre O and ∠QPR = 50°.
To find: ∠QSR
∠QOR + ∠QPR =180°
⇒ ∠QOR +50° = 180°
⇒ ∠QOR = 130°
⇒ ∠QSR = 12 ∠QOR [Degree measure theorem]
⇒ ∠QSR =12 × 130° = 65°
Circle MCQ Question 35. In the given figure, AB, AC and AD are tangents. If AB = 5 cm, find AD.
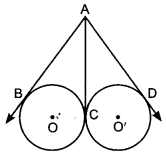
Answer/ Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Given: AB, AC and AD are tangents. AB = 5 cm.
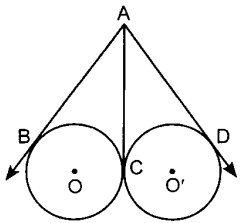
To find: AD
Sol. AB and AC are tangents from the same point to the circle with centre O.
⇒ AB = AC …(i)
(Length of the tangents from the same external point are equal).
AC and AD are tangents from the same point to the circle with centre O.
⇒ AC = AD …(ii)
(Length of the tangents from the same external point are equal)
From (i) and (ii)
∵ AB = AC = AD = 5 cm
We hope the given MCQ Questions for Class 10 Maths Circles with Answers will help you. If you have any query regarding CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circles Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.